What are the benefits of crop rotation in sustainable farming?
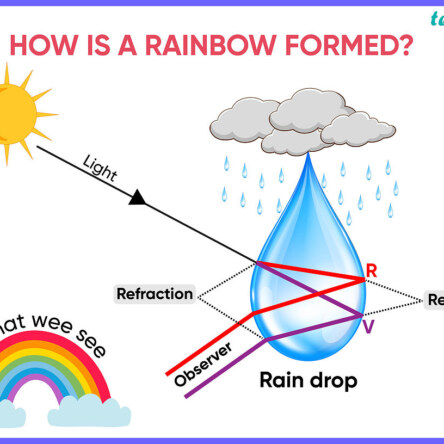
Rainbows form when sunlight passes through water droplets in the atmosphere, causing the light to refract, reflect, and disperse into the colors of the spectrum: Refraction: When light passes from air into a denser medium, like a raindrop, it changes direction. This is called refraction. Reflection:Read more
Rainbows form when sunlight passes through water droplets in the atmosphere, causing the light to refract, reflect, and disperse into the colors of the spectrum:
Refraction: When light passes from air into a denser medium, like a raindrop, it changes direction. This is called refraction.
Reflection: The light reflects off the back of the raindrop.
Dispersion: The light disperses into the seven colors of the spectrum.
For a rainbow to appear, the sun, raindrops, and the observer must be in the right positions:
The sun must be behind the viewer.
The sun must be low in the sky, at an angle of less than 42° above the horizon.
Rain, fog, or some other source of water droplets must be in front of the viewer.
Rainbows appear semi-circular over level ground at sunrise or sunset. When viewed from the air, rainbows form a complete circle.









The meaning of Crop rotation is the practice of growing different crops in a specific order on the same land over multiple seasons. The goal of crop rotation is to maintain the soil's productivity by preventing it from being used for only one set of nutrients. Crop rotation can have many benefits, iRead more
The meaning of Crop rotation is the practice of growing different crops in a specific order on the same land over multiple seasons. The goal of crop rotation is to maintain the soil’s productivity by preventing it from being used for only one set of nutrients.
See lessCrop rotation can have many benefits, including:
Soil health: Improves soil structure, fertility, and organic matter
Pest and disease control: Breaks the life cycle of pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides
Weed growth: Reduces weed growth
Crop yield: Increases crop yield
Labor efficiency: Distributes labor more evenly throughout the seasons
A simple rotation might involve two or three crops, while a complex rotation might include a dozen or more. For example, a farmer might plant beans after harvesting corn because corn uses a lot of nitrogen and beans return nitrogen to the soil.