What are the building blocks of proteins?
Cross cousin marriages and parallel cousin marriages are terms used in anthropology and sociology to describe marriage practices based on specific types of cousin relationships. Here's the distinction: 1. Cross Cousin Marriages Definition: A marriage between a person and their cross cousin. Cross coRead more
Cross cousin marriages and parallel cousin marriages are terms used in anthropology and sociology to describe marriage practices based on specific types of cousin relationships. Here’s the distinction:
1. Cross Cousin Marriages
- Definition: A marriage between a person and their cross cousin. Cross cousins are the children of one’s parent’s opposite-sex sibling.
- For example:
- A mother’s brother’s children (maternal uncle’s children).
- A father’s sister’s children (paternal aunt’s children).
- For example:
- Cultural Context: Cross cousin marriages are common in some cultures because they are seen as promoting alliances between different family groups.
- Examples of Societies:
- Found in many tribal societies, such as those in South India, parts of Africa, and among Australian Aboriginal groups.
2. Parallel Cousin Marriages
- Definition: A marriage between a person and their parallel cousin. Parallel cousins are the children of one’s parent’s same-sex sibling.
- For example:
- A mother’s sister’s children (maternal aunt’s children).
- A father’s brother’s children (paternal uncle’s children).
- For example:
- Cultural Context: Parallel cousin marriages are less common and are often discouraged in many societies because these cousins are considered part of the same lineage or close kinship group.
- Examples of Societies:
- Found in some Islamic cultures and certain communities in the Middle East.
Key Differences
| Feature | Cross Cousin Marriage | Parallel Cousin Marriage |
|---|---|---|
| Relation | Opposite-sex sibling’s children | Same-sex sibling’s children |
| Kinship Perspective | Seen as creating alliances between groups | Often remains within the same lineage or group |
| Prevalence | More widely accepted in various societies | Less common and culturally restricted |
Anthropological Significance
These marriage patterns reflect how societies view kinship, inheritance, and alliances. Cross cousin marriages often serve to strengthen ties between different family branches, while parallel cousin marriages are more about maintaining family unity or lineage continuity.
See less
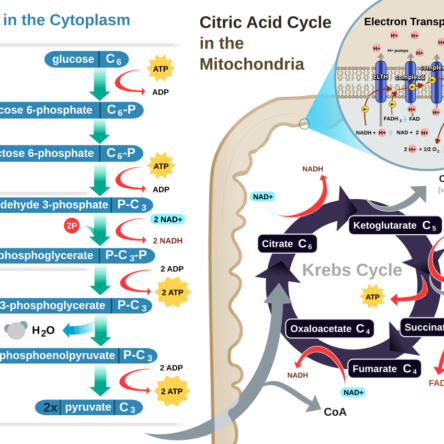








The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules. Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form long chains called polypeptides. Many polypeptides join to form a protein. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure. Proteins aRead more
The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules.
See lessAmino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form long chains called polypeptides. Many polypeptides join to form a protein. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure.
Proteins are important for many functions in the body, including:
Structural elements: Proteins provide many of the structural elements of a cell and help bind cells together into tissues
Chemical reactions: Proteins catalyze most of the chemical reactions that occur in a cell
Transport: Proteins transport nutrients
Hormones and enzymes: Proteins function as hormones and enzymes