How CIBIL score is calculated ?
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
See lessSign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
At Qukut, our mission is to bridge the gap between knowledge seekers and knowledge sharers. We strive to unite diverse perspectives, fostering understanding and empowering everyone to contribute their expertise. Join us in building a community where knowledge flows freely and growth is limitless.
What is the significance of the Bhagavad Gita in Hinduism?
What is the speed of light?
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
See lessWhat is the function of red blood cells?
The primary function of red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and carry carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs for exhalation. Here are the key functions of RBCs: 1. Oxygen Transport: Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protRead more
The primary function of red blood cells (RBCs), or erythrocytes, is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues and carry carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs for exhalation. Here are the key functions of RBCs:
1. Oxygen Transport: Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen in the lungs. Each hemoglobin molecule can carry up to four oxygen molecules, allowing RBCs to efficiently transport oxygen to various tissues and organs throughout the body.
2. Carbon Dioxide Transport: Red blood cells also play a crucial role in removing carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, from the body. They transport some carbon dioxide back to the lungs for exhalation, while a portion of it is converted into bicarbonate ions in the plasma.
3. Maintaining Acid-Base Balance: By regulating carbon dioxide levels and converting it into bicarbonate ions, red blood cells help maintain the pH balance of the blood, which is essential for normal cellular functions.
4. Delivering Nutrients and Removing Waste: Although primarily involved in gas transport, red blood cells also contribute to the delivery of nutrients and the removal of metabolic waste products.
5. Maintaining Blood Viscosity and Pressure: The number of red blood cells influences blood viscosity, which affects blood pressure and flow. Proper RBC levels are vital for maintaining adequate circulation and oxygenation of tissues.
In summary, red blood cells are essential for carrying oxygen to tissues, removing carbon dioxide, and contributing to overall blood function and homeostasis.
See lessHow does altitude affect endurance in long-distance running?
Altitude significantly affects endurance in long-distance running due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Here's a detailed breakdown of how altitude impacts performance: Reduced Oxygen Availability At higher altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is lower, which leads to a decrease in the partial pRead more
Altitude significantly affects endurance in long-distance running due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how altitude impacts performance:
Altitude poses a challenge to endurance in long-distance running by limiting oxygen availability, but with proper acclimatization, athletes can adapt and potentially gain a competitive edge when returning to lower altitudes.
See lessWhich country eats the tastiest food in the world
There is no definitive answer to which country has the "tastiest food," as taste is subjective and varies greatly depending on personal preferences, cultural background, and individual experiences. However, several countries are renowned worldwide for their diverse and flavorful cuisines, often makiRead more
There is no definitive answer to which country has the “tastiest food,” as taste is subjective and varies greatly depending on personal preferences, cultural background, and individual experiences. However, several countries are renowned worldwide for their diverse and flavorful cuisines, often making it to the top of food rankings:
1. Italy – Known for its pasta, pizza, and rich sauces like marinara and pesto, Italian cuisine is beloved worldwide for its simplicity and quality ingredients.
2. Japan – Japanese cuisine, particularly sushi, ramen, and tempura, is appreciated for its balance of flavors, fresh ingredients, and presentation.
3. Mexico – Mexican food, including tacos, enchiladas, and guacamole, is celebrated for its bold flavors, spices, and variety of fresh ingredients.
4. India – Indian cuisine is known for its complex use of spices, with dishes like curry, biryani, and samosas, offering rich flavors and diverse regional variations.
5. France – Famous for fine dining, French cuisine includes delicacies like croissants, escargot, and a wide range of cheeses, sauces, and wines.
Ultimately, the “tastiest” food depends on what flavors and cooking styles resonate with you personally. Each country offers something unique and delicious!
See lessHow do different organisms adapt to their environment?
Different organisms adapt to their environment through a variety of strategies, allowing them to survive and thrive in their specific habitats. These adaptations can be structural, behavioral, or physiological, and they help organisms meet the challenges posed by their surroundings. Here are some exRead more
Different organisms adapt to their environment through a variety of strategies, allowing them to survive and thrive in their specific habitats. These adaptations can be structural, behavioral, or physiological, and they help organisms meet the challenges posed by their surroundings. Here are some examples of how organisms adapt:
These are physical features of an organism’s body that enhance survival in its environment.
These are actions organisms take to increase their chances of survival.
These are internal changes that allow organisms to function optimally in their environment.
Over long periods, populations of organisms undergo natural selection, leading to adaptations that improve their overall survival and reproduction.
Some organisms are adapted to extreme conditions such as high heat, deep pressure, or no light.
Plants also exhibit unique adaptations to survive in their environment.
Organisms adapt to their environment through a combination of structural, behavioral, and physiological changes. These adaptations allow them to cope with various challenges such as temperature, food availability, predation, and environmental extremes, ensuring their survival and reproduction in a dynamic world. Adaptations are often the result of evolutionary processes, and over time, they help organisms become better suited to their specific habitats.
See lessIn which one of the following regions was Dhanyakataka, which flourished as a prominent Buddhist centre under the Mahasanghikas, located? ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
Dhanyakataka was a significant ancient city that emerged as a prominent Buddhist center, particularly under the Mahasanghikas, an early Buddhist sect. This city is primarily associated with the region of Andhra. Historical Context Location and Significance: Dhanyakataka is believed to have been locaRead more
Dhanyakataka was a significant ancient city that emerged as a prominent Buddhist center, particularly under the Mahasanghikas, an early Buddhist sect. This city is primarily associated with the region of Andhra.
Historical Context
The correct answer to the question “In which one of the following regions was Dhanyakataka, which flourished as a prominent Buddhist center under the Mahasanghikas, located?” is Andhra. The city’s historical and cultural significance, combined with its role as a center of Buddhist learning and practice, highlights its importance in the broader context of Indian history and the spread of Buddhism.
See lessfirst one open the app and go to setting and scroll down with saw the sharing of this app this is feature
first one open the app and go to setting and scroll down with saw the sharing of this app this is feature
See lessHow many of the given statements regarding green hydrogen is/are correct? [2023]1. It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion.2. It can ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
Correct Answer: All three Explanation: It can be used directly as a fuel for internal combustion: Correct. Green hydrogen can be used as a fuel in internal combustion engines (ICEs) with modifications. Hydrogen combusts cleanly, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct, making it a potential alternaRead more
Thus, all three statements are correct.
See lessConsider the following statements: ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
Let's break down the statements: The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger (Guizotia abyssinica) seeds: This is correct. Niger seeds are one of the crops for which the Government of India declares a Minimum Support Price (MSP) to support farmers. Niger is cultivated as a KhariRead more
Let’s break down the statements:
Thus, all three statements are correct. Therefore, the correct answer is All three.
See lessHow is the celebration of Corpus Christi and Transubstantiation related to the development of English drama??
The celebration of Corpus Christi and the doctrine of Transubstantiation were deeply intertwined with the development of English drama, particularly in the Middle Ages. Here's how they are connected: 1. Corpus Christi Feast and Liturgical Drama Corpus Christi is a feast celebrating the belief in theRead more
The celebration of Corpus Christi and the doctrine of Transubstantiation were deeply intertwined with the development of English drama, particularly in the Middle Ages. Here’s how they are connected:
The celebration of Corpus Christi and its focus on Transubstantiation provided the theological and cultural foundation for the mystery play cycles, which became a pivotal phase in the evolution of English drama. These plays not only taught religious doctrine but also laid the groundwork for theatrical traditions that evolved into the rich tapestry of English Renaissance drama.
See lessHow is Nested Class different from Inheritance?
A nested class is not the same as an inherited class. Let’s see why with simple examples. Nested Classes A nested class is just a class declared inside another class. (a) Static Nested Class class School { static class Student { void showDetails() { System.out.println("I am a student of the school."Read more
A nested class is not the same as an inherited class. Let’s see why with simple examples.
A nested class is just a class declared inside another class.
(a) Static Nested Class
class School {
static class Student {
void showDetails() {
System.out.println(“I am a student of the school.”);
}
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School.Student s = new School.Student();
s.showDetails();
}
}
(b) Inner Class (Non-static)
class School {
class Teacher {
void display() {
System.out.println(“I am a teacher of the school.”);
}
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
School school = new School();
School.Teacher t = school.new Teacher();
t.display();
}
}
Inheritance happens when one class extends another.
class Person {
void displayInfo() {
System.out.println(“I am a person.”);
}
}
class Student extends Person {
void showDetails() {
System.out.println(“I am a student.”);
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.displayInfo(); // inherited from Person
s.showDetails(); // defined in Student
}
}
What is the true purpose of human existence?
The true purpose of human existence is a deeply philosophical question, and the answer can vary depending on one's beliefs, cultural perspectives, and individual experiences. Several schools of thought offer different perspectives on the matter: 1. Philosophical Perspectives Existentialism: ThinkersRead more
The true purpose of human existence is a deeply philosophical question, and the answer can vary depending on one’s beliefs, cultural perspectives, and individual experiences. Several schools of thought offer different perspectives on the matter:
1. Philosophical Perspectives
Existentialism: Thinkers like Jean-Paul Sartre and Albert Camus suggest that life inherently lacks a predefined purpose. Instead, individuals must create their own meaning through choices, actions, and personal freedom.
Absurdism: Albert Camus also introduced the concept of absurdism, arguing that humans naturally seek meaning in a chaotic, indifferent universe. While the search for meaning may seem futile, embracing the absurdity and continuing to live fully is a form of personal liberation.
Humanism: From a humanist perspective, the purpose of life may be to seek fulfillment through personal growth, the improvement of society, and the pursuit of knowledge and happiness.
2. Religious Perspectives
Christianity: In Christian doctrine, the purpose of human life is often seen as fulfilling God’s will, following the teachings of Jesus Christ, and striving for salvation through faith, love, and compassion.
Hinduism: Hindu philosophy suggests that life’s purpose is to attain moksha (liberation from the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth) through righteous living, self-discipline, meditation, and devotion to God.
Buddhism: In Buddhism, the purpose is to achieve nirvana (enlightenment), which involves overcoming suffering and the cycle of rebirth by following the Eightfold Path, emphasizing ethical conduct, meditation, and wisdom.
Islam: In Islam, human existence is believed to be a test from God (Allah), where the purpose is to worship Him, lead a moral life, and prepare for an eternal life in the afterlife.
3. Scientific and Evolutionary Perspectives
Biological Evolution: From an evolutionary standpoint, the “purpose” of human existence could be seen as the continuation of the species through reproduction and the passing on of genetic material. However, many scientists also acknowledge that humans have the capacity for self-awareness, morality, and creating purpose beyond survival instincts.
Cosmology and the Universe: Some scientists approach the question from a cosmological angle, arguing that human existence is an outcome of the natural processes of the universe. In this context, humans are just one part of an immense, ever-evolving universe with no intrinsic purpose other than what individuals assign to their lives.
4. Personal Meaning and Fulfillment
Many people find purpose in personal experiences and relationships. The pursuit of happiness, fulfillment, and making meaningful contributions to the well-being of others are often seen as vital aspects of a person’s life purpose. This may involve creating art, raising a family, advancing knowledge, or helping others achieve their potential.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the true purpose of human existence is subjective and multifaceted. It may be a combination of the search for personal meaning, contributing to society, spiritual growth, or the pursuit of knowledge. While some may find purpose in religious faith, others in personal development, and still others in social impact, the beauty of this question lies in the fact that every individual has the ability to define their own path and purpose.
See lessThe ‘Higgs Boson’ particle was confirmed in which year?
Please login to vote and see the results.
The Higgs Boson particle was confirmed in 2012 by scientists at CERN using the Large Hadron Collider.
The Higgs Boson particle was confirmed in 2012 by scientists at CERN using the Large Hadron Collider.
See lessWhat are the various natural vegetations of North America
How does gravity work on different planets?
Gravity works on all planets by the same fundamental principle: it is a force of attraction that pulls objects toward the center of a planet. The strength of this gravitational pull depends on the planet's mass and radius. Here's how gravity varies across different planets: Key Factors Affecting GraRead more
Gravity works on all planets by the same fundamental principle: it is a force of attraction that pulls objects toward the center of a planet. The strength of this gravitational pull depends on the planet’s mass and radius. Here’s how gravity varies across different planets:
| Planet | Surface Gravity (compared to Earth) |
|---|---|
| Mercury | 0.38 times Earth’s gravity |
| Venus | 0.91 times Earth’s gravity |
| Earth | 1.00 (standard gravity) |
| Mars | 0.38 times Earth’s gravity |
| Jupiter | 2.34 times Earth’s gravity |
| Saturn | 1.06 times Earth’s gravity |
| Uranus | 0.92 times Earth’s gravity |
| Neptune | 1.19 times Earth’s gravity |
The variation in gravity affects how objects fall, how much they weigh, and the way we move on different planets. For example, you would weigh much less on Mars than on Earth but much more on Jupiter.
See lessThe village known as "The Most Haunted Village of India" is Kuldhara, located near Jaisalmer in Rajasthan. Kuldhara is often referred to as a ghost village due to its abandoned state and the legends surrounding its desolation. According to local lore, the village was once home to the Paliwal BrahminRead more
The village known as “The Most Haunted Village of India” is Kuldhara, located near Jaisalmer in Rajasthan. Kuldhara is often referred to as a ghost village due to its abandoned state and the legends surrounding its desolation. According to local lore, the village was once home to the Paliwal Brahmins, who fled overnight in 1825 to escape the oppressive demands of a local minister, leaving behind a curse that no one would ever be able to inhabit the village again.
While Kuldhara is recognized for its haunted reputation, it’s worth noting that Bhangarh Fort is frequently cited as the most haunted place in India, although it was not included in your options. The stories and eerie atmosphere surrounding both locations attract many visitors interested in the supernatural.
See lessWhat are interrogatory words and how to use them?
Interrogatory words are used to ask questions in English. They are also called question words because they often begin sentences that seek information. These words help gather details about various aspects of a subject, such as people, time, place, reason, method, or quantity. Common Interrogatory WRead more
Interrogatory words are used to ask questions in English. They are also called question words because they often begin sentences that seek information. These words help gather details about various aspects of a subject, such as people, time, place, reason, method, or quantity.
By using these words appropriately, you can frame clear, concise, and effective questions in both spoken and written communication.
See lessWhat is the difference between a compound and a mixture?
Difference between compound and mixture are: Aspect Compound Mixture Definition A substance formed from two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. A combination of two or more substances that are physically combined. Chemical Bonds Elements are bonded together by chemical bonds (Read more
Difference between compound and mixture are:
| Aspect | Compound | Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A substance formed from two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions. | A combination of two or more substances that are physically combined. |
| Chemical Bonds | Elements are bonded together by chemical bonds (covalent or ionic). | No chemical bonds; components retain their own properties. |
| Properties | Has new, distinct properties different from its constituent elements. | The individual properties of the components are retained. |
| Separation | Can only be separated by a chemical process (e.g., electrolysis, heating). | Can be separated by physical means (e.g., filtration, distillation). |
| Proportion of Components | Fixed and definite proportions of elements. | Proportions of components can vary. |
| Example | Water (H₂O), Sodium chloride (NaCl) | Air, Salad, Sand and salt mixture |
Why only the cells in the first row of Heat Map displaying annotation not the other cells?
This issue could be due to an outdated version of Seaborn. You can resolve it by updating Seaborn with the following command: pip install seaborn --upgrade
This issue could be due to an outdated version of Seaborn. You can resolve it by updating Seaborn with the following command:
pip install seaborn --upgrade
What are the types of simple machines?
Who is Himani Mor?
Himani Mor is a notable Indian tennis player and the wife of Olympic javelin champion Neeraj Chopra. Here’s a concise overview of her life and career: Born on June 26, 1999, in Larsauli village, Sonipat, Haryana, Himani was encouraged to pursue tennis from a young age. She attended Little Angels SchRead more
Himani Mor is a notable Indian tennis player and the wife of Olympic javelin champion Neeraj Chopra. Here’s a concise overview of her life and career:
Born on June 26, 1999, in Larsauli village, Sonipat, Haryana, Himani was encouraged to pursue tennis from a young age. She attended Little Angels School and later studied Political Science and Physical Education at Miranda House, Delhi University. She furthered her education in Sports Management at Franklin Pierce University in the United States.
Himani has made significant contributions to Indian tennis, achieving rankings of 42nd in singles and 27th in doubles according to the All India Tennis Association (AITA). Her competitive journey includes participation in various national and international tournaments.
In addition to her playing career, she has taken on coaching roles. Himani served as a Volunteer Assistant Tennis Coach at Franklin Pierce University and is currently a Graduate Assistant at Amherst College, where she manages the women’s tennis team.
Himani gained media attention after marrying Neeraj Chopra on January 18, 2025. Their relationship symbolizes a union of two celebrated athletes, attracting significant public interest.
At just 25 years old, Himani Mor exemplifies dedication in both sports and academics. Her journey inspires many young athletes, particularly women, as she balances her professional aspirations with her new role as a supportive partner to Neeraj Chopra.
See lessConsider the following statements: ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InVITs) gather funds from investors, which are subsequently directed into infrastructure projects. As pooled investment vehicles, they function similarly to mutual funds. However, while mutual funds predominantly invest in stocks and bonds, InVITs focus on infrastruRead more
Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InVITs) gather funds from investors, which are subsequently directed into infrastructure projects. As pooled investment vehicles, they function similarly to mutual funds. However, while mutual funds predominantly invest in stocks and bonds, InVITs focus on infrastructure-related ventures. The returns generated by InVITs are distributed to investors through four primary methods: interest on capital, dividends, rental income, and repayment of capital. Previously, interest, dividends, and rental income earned by unit holders were taxable, but repayment of capital was exempt from tax. However, the Finance Act of 2023 introduced a provision to tax certain portions of capital repayment in specific cases, making Statement 1 incorrect. Additionally, the Finance Act of 2021 amended the SARFAESI Act of 2002 to recognize pooled investment vehicles, including REITs and InVITs, as borrowers under the Act, making Statement 2 correct.
Therefore, the correct answer is Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct.
See lessdiscuss the working of heart in detail
The heart is a muscular organ that functions as the central component of the circulatory system, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Its primary role is to supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and remove carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes. The heart operates in a highly coordRead more
The heart is a muscular organ that functions as the central component of the circulatory system, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Its primary role is to supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and remove carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes. The heart operates in a highly coordinated manner, with distinct phases of contraction and relaxation. Here’s a detailed discussion on how the heart works:
The heart consists of four chambers:
The heart also contains several valves that control the flow of blood and prevent backflow:
The heart works through a continuous cycle of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole). The cycle ensures that blood flows in the right direction and is efficiently pumped throughout the body.
The heart’s pumping action is controlled by an electrical system that ensures the chambers contract in a coordinated manner. The major components of this system are:
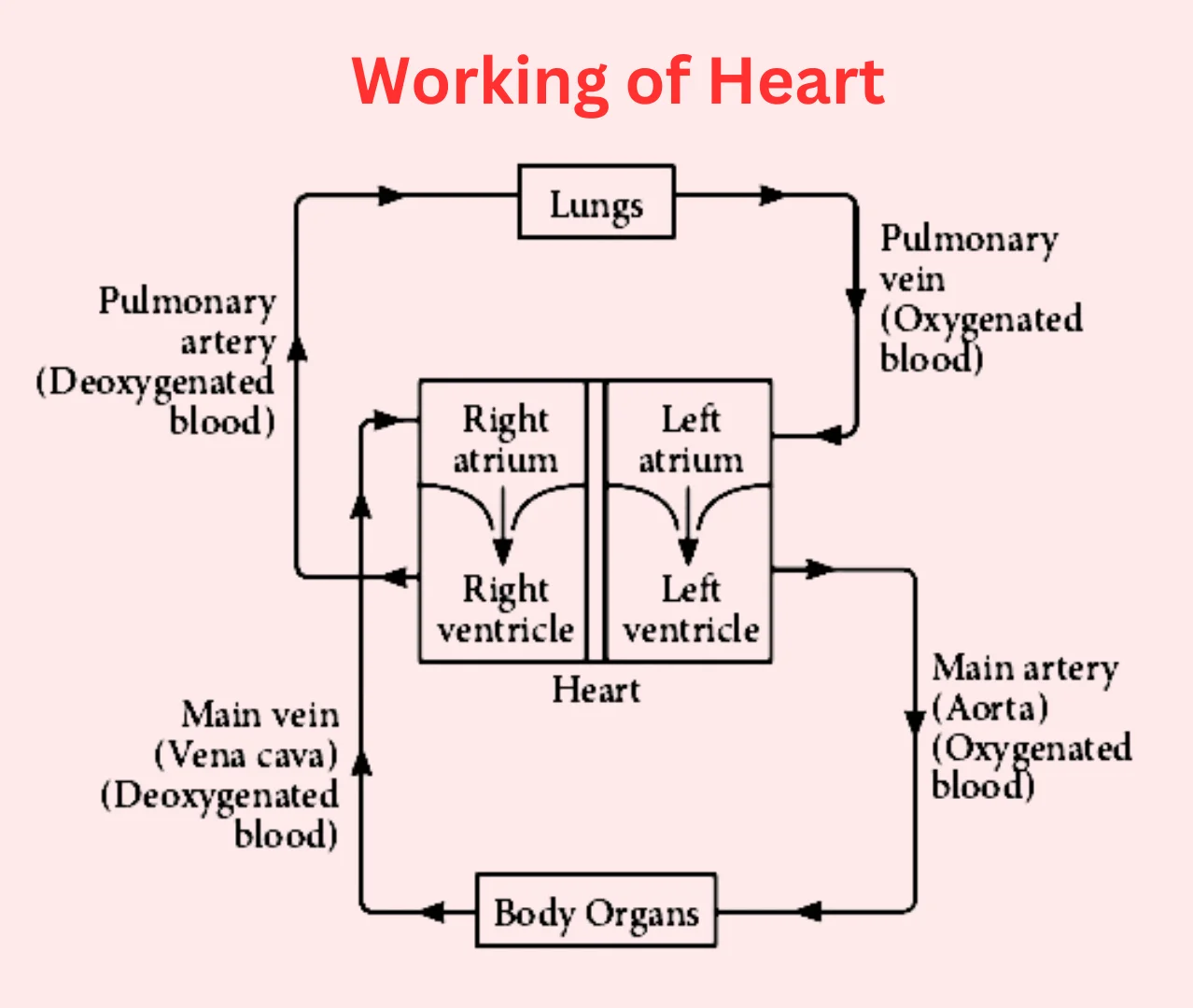
The heart rate is controlled by a combination of:
The heart can be affected by various diseases and conditions, including:
The heart functions as a pump that circulates blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. Its intricate structure, along with its electrical and mechanical coordination, allows it to operate efficiently. Proper heart function is vital for overall health, and any disturbances in its working can lead to serious health conditions.
See lessBecoming an Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer is a highly respected achievement and requires dedication, hard work, and strategic preparation. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to become an IAS officer: 1. Eligibility Criteria: Educational Qualification: You must hold a bachelor's degreeRead more
Becoming an Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer is a highly respected achievement and requires dedication, hard work, and strategic preparation. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to become an IAS officer:
The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) conducts the Civil Services Examination (CSE) every year to select candidates for IAS, IPS, and other civil services posts. The exam is a three-stage process:
Becoming an IAS officer requires more than just academic knowledge—it demands determination, resilience, and a strong desire to serve the nation. While the journey is challenging, with proper planning, dedication, and consistent effort, you can achieve this prestigious goal.
See lessDescribe in detail the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders and international classification of diseases?
The ICD is the official world classification. The section concerned with psychiatric disorders is called ‘Mental and Behavioural Disorders’. This classification is used to record the diagnoses of all patients seen in psychiatric care across the world where official statistics are collected. By contrRead more
The ICD is the official world classification. The
section concerned with psychiatric disorders is
called ‘Mental and Behavioural Disorders’. This
classification is used to record the diagnoses of all
patients seen in psychiatric care across the world
where official statistics are collected. By contrast,
the DSM is the official classification in the USA
for clinical diagnosis, although its influence
now covers the globe, particularly because of its
apparent advantages for research and the general
belief that it is in some way more accurate.
DSM is mainly used by psychiatrists, although it
is recognising that this is not entirely satisfactory
and is promoting its use among psychologists
and other mental health practitioners. ICD, on
the other hand, has always had in mind the
universal mental health practitioner.
DSM has been productive in promoting research,
but has handicapped advances in some respects by
giving credibility to diagnoses which probably do
not exist, and has generated much needless research into issues such as comorbidity of disorders which share much more than they differ by.
ICD has been poorly resourced and has not been
able to generate the same degree of research data
as DSM, but has steadily improved over the years
and, with better descriptions and definitions, is
likely to be used not only widely, but more seriously
and accurately.
Can anyone earn money at sitting home by using phone?
Yes, many people can earn money from home using just their phone. Here are some popular methods: Freelancing Platforms: Websites like Fiverr, Upwork, and Freelancer allow you to offer services such as writing, graphic design, programming, social media management, and more. How to Start: Create a proRead more
Yes, many people can earn money from home using just their phone. Here are some popular methods:
Each of these options requires different levels of skill, time commitment, and initial investment, but they can all be done from the comfort of your home using just your phone.
See lessWhat is “mixture of experts” ?
A Mixture of Experts (MoE) is a machine learning architecture designed to improve model performance and efficiency by combining specialized "expert" sub-models. Instead of using a single monolithic neural network, MoE systems leverage multiple smaller networks (the "experts") and a gating mechanism Read more
A Mixture of Experts (MoE) is a machine learning architecture designed to improve model performance and efficiency by combining specialized “expert” sub-models. Instead of using a single monolithic neural network, MoE systems leverage multiple smaller networks (the “experts”) and a gating mechanism that dynamically routes inputs to the most relevant experts. Here’s a breakdown:
MoE is a cornerstone of cost-effective AI scaling. For example:
What are the key strategies in professional curling?

Introduction: The Eternal Hymn of Detachment and Devotion Shiv Rudrashtakam is one of the most profound Sanskrit hymns dedicated to Lord Shiva, the supreme yogi, destroyer of ignorance, and embodiment of pure consciousness. Composed by Adi Shankaracharya, this eight-verse stotra ...

A Prime-Adam Number is defined as a positive number that fulfills two conditions simultaneously: it is a prime number and also an Adam number. For example, take the number 13; its reverse is 31. The square of 13 is 169, and the ...

Introduction The 74th Miss Universe pageant, held on November 21, 2025, at the Impact Challenger Hall in Nonthaburi, Thailand, set a new benchmark in global beauty contests. Not merely a showcase of beauty and fashion, this year’s event stood as ...

A Keith number is an n-digit number that appears as a term in a sequence, where the first n terms are its own digits, and each following term is the sum of the previous n terms. For example, 197 is ...

A matrix is called Doubly Markov if it satisfies the following conditions: All elements are greater than or equal to 0. The sum of each row is equal to 1. The sum of each column is equal to 1. The program should ...

The Dawn of a Clean Energy Revolution Imagine a world where air pollution is history, industries run clean, and the very fuel that powers our lives leaves nothing behind but water vapor. Sounds like science fiction? It’s the promise of ...
The CIBIL score (Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited score) is a three-digit number that represents an individual's creditworthiness. It is calculated based on the data in the individual's credit report. Here's a detailed breakdown of how the CIBIL score is calculated: 1. Components of CIBIL SRead more
The CIBIL score (Credit Information Bureau (India) Limited score) is a three-digit number that represents an individual’s creditworthiness. It is calculated based on the data in the individual’s credit report. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how the CIBIL score is calculated:
1. Components of CIBIL Score
The CIBIL score is typically influenced by the following factors:
A. Payment History (35%)
Timely repayment of loans and credit card bills positively impacts the score.
Delayed payments, defaults, or settlements reduce the score.
B. Credit Utilization (30%)
The proportion of credit used compared to the total credit limit.
High utilization indicates dependency on credit, which negatively affects the score.
C. Credit Mix and Duration (25%)
The diversity of credit accounts (secured loans like home/car loans and unsecured loans like credit cards/personal loans) improves the score.
Longer credit history with consistent repayment behavior increases the score.
D. Number of Hard Inquiries (10%)
Frequent applications for loans or credit cards result in hard inquiries by lenders, which can lower the score.
Multiple inquiries in a short period signal credit hunger, affecting the score negatively.
2. Key Metrics in Credit Report
Account Age: Older credit accounts demonstrate long-term financial reliability.
Debt-to-Income Ratio: Lower ratios indicate better financial health.
Negative Records: Loan defaults, write-offs, or bankruptcies have a significant adverse impact.
3. Weightage of Factors
Payment history holds the highest weightage, reflecting your reliability in repaying debts.
A balanced mix of secured and unsecured credit and a longer credit history contribute significantly to a high score.
4. Score Range
300–549: Poor (Credit applications are usually denied).
550–649: Average (Higher chances of loan rejection).
650–749: Good (Eligible for loans, but at higher interest rates).
750–900: Excellent (Easily approved for loans with favorable terms).
How to Monitor Your CIBIL Score?
Obtain a free annual CIBIL report from the CIBIL website or authorized financial institutions.
Regularly monitor for discrepancies or errors in your credit report and report them for rectification.
By maintaining a disciplined financial approach—timely payments, low credit utilization, and a good credit mix—you can ensure a healthy CIBIL score.
See less