What happens inside a black hole beyond the event horizon?
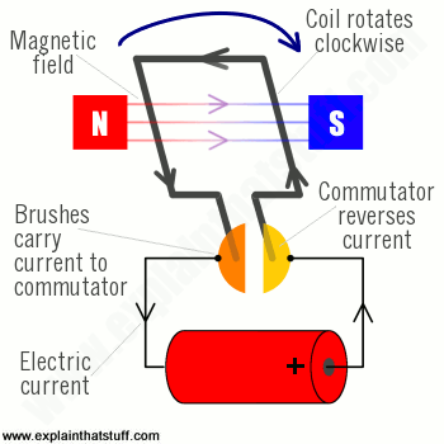
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by using the interaction of magnetic fields and electric current: Magnetic field: The stator, the stationary part of the motor, generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. Rotor: The rotor, the rotating paRead more
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by using the interaction of magnetic fields and electric current:
Magnetic field: The stator, the stationary part of the motor, generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it.
Rotor: The rotor, the rotating part of the motor, interacts with the magnetic field, which causes it to spin.
Shaft: The spinning rotor drives a shaft, which creates mechanical motion.
Electric motors can be powered by either alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). The main difference between the two is that AC motors use alternating current, which changes direction.
Electric motors have many different parts, including: stator, rotor, commutator, power source, and brushes.
The opposite of an electric motor is an electric generator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.

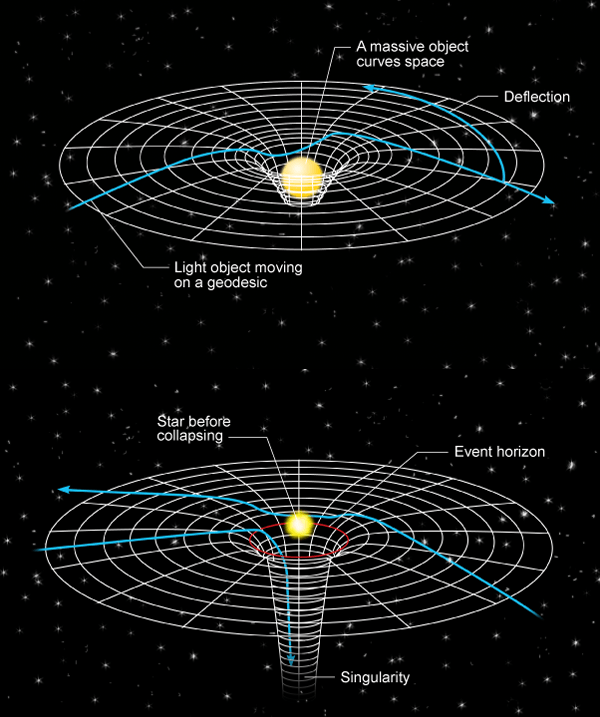






Once matter passes the event horizon of a black hole, it's torn apart and crushed into a singularity. At the singularity, the laws of physics as we know them no longer apply. What happens to matter inside a black hole? Spaghettification: The matter is stretched into long strands, similar to pasta, aRead more
Once matter passes the event horizon of a black hole, it’s torn apart and crushed into a singularity. At the singularity, the laws of physics as we know them no longer apply.
See lessWhat happens to matter inside a black hole?
Spaghettification: The matter is stretched into long strands, similar to pasta, and ripped apart by the gravitational forces
Superheating: The matter is superheated and emits X-rays
Crushing: The matter is crushed into a singularity, a one-dimensional point at the center of the black hole
What happens to time inside a black hole?
Time dilation: Time passes more slowly near a strong gravitational source
Space-time flow: Space-time flows inward at the speed of light at the event horizon
What happens to the black hole?
Hawking radiation
Black holes may slowly radiate energy away, which could cause them to evaporate over time
Size
The size of the black hole’s event horizon increases as more matter accumulates at the singularity