Which one of the following activities of the Reserve Bank of India is considered to be part of ‘sterilization? ...Read more
Poll Results
Please login to vote and see the results.
Sign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
At Qukut, our mission is to bridge the gap between knowledge seekers and knowledge sharers. We strive to unite diverse perspectives, fostering understanding and empowering everyone to contribute their expertise. Join us in building a community where knowledge flows freely and growth is limitless.
स्वस्थ रहने के लिए क्या आहार लें?
To stay healthy, a balanced diet is essential. A balanced diet includes the right proportion of nutrients required by the body. Here are key recommendations for a healthy diet: 1. Include a Variety of Foods Fruits and Vegetables: Consume at least 5 servings a day. Choose a variety of colors for diffRead more
To stay healthy, a balanced diet is essential. A balanced diet includes the right proportion of nutrients required by the body. Here are key recommendations for a healthy diet:
By following these guidelines, you can maintain overall health, energy levels, and immunity while reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
See lessIdentify the next number: 2, 6, 12, 20, 30, ___
the next term is 42
the next term is 42
See less“Souls are not only the property of animal and plant life, but also of rocks, running water and many other natural objects not looked on as living by other religious sects.” ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
The statement reflects one of the core beliefs of Jainism. Jainism emphasizes the idea that all living beings, including plants, animals, and even non-living entities like rocks and water, possess souls (jiva) and that all life is interconnected. This belief in the sanctity of all forms of life is fRead more
The statement reflects one of the core beliefs of Jainism.
Jainism emphasizes the idea that all living beings, including plants, animals, and even non-living entities like rocks and water, possess souls (jiva) and that all life is interconnected. This belief in the sanctity of all forms of life is fundamental to Jain philosophy and ethics.
See lessWhich books are known to broaden one’s perspective?
Books That Broaden Perspectives: A Thoughtful Selection 1. “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari Why it broadens perspective: Offers a sweeping, interdisciplinary look at human history, combining anthropology, biology, and economics to question how societies and civilizationsRead more
Why it broadens perspective: Offers a sweeping, interdisciplinary look at human history, combining anthropology, biology, and economics to question how societies and civilizations evolved.
Unique insight: Challenges the reader to rethink human progress, culture, and the meaning of happiness.
Why it broadens perspective: Explores the dual systems of human thought — intuitive vs. analytical — shedding light on cognitive biases and decision-making.
Unique insight: Reveals how our minds work and why we often err, fostering self-awareness and critical thinking.
Why it broadens perspective: Combines Eastern philosophy and Western psychology to explore what true happiness means.
Unique insight: Encourages empathy, compassion, and mindfulness as tools for personal and collective growth.
Why it broadens perspective: Investigates the environmental and geographical reasons behind the unequal development of human societies.
Unique insight: Challenges simplistic explanations of history, emphasizing complex global interconnections.
Why it broadens perspective: A philosophical novel exploring absurdism and existentialism.
Unique insight: Invites readers to confront meaning, alienation, and individual freedom in a seemingly indifferent universe.
Why it broadens perspective: A memoir blending humor and tragedy, revealing the complexities of apartheid and post-apartheid South Africa.
Unique insight: Offers a deeply personal view of systemic racism, identity, and resilience.
Why it broadens perspective: Foundational feminist text analyzing the social construction of gender.
Unique insight: Provokes rethinking of gender roles, equality, and personal freedom.
Why it broadens perspective: Stoic philosophy from a Roman emperor’s personal reflections on life, duty, and virtue.
Unique insight: Promotes resilience, ethical living, and clarity of thought.
Why it broadens perspective: A historical novel narrated by Death, exploring humanity during WWII.
Unique insight: Highlights the power of words and the complexity of human morality amid conflict.
Why it broadens perspective: Addresses African American identity and invisibility in society.
Unique insight: Unpacks race, individuality, and social injustice in mid-20th-century America.
Cross-cultural understanding: They expose readers to diverse histories, philosophies, and social realities.
Critical thinking: They challenge ingrained biases and encourage questioning assumptions.
Emotional intelligence: They foster empathy through personal stories and ethical reflections.
Philosophical depth: They engage with existential questions about meaning, identity, and society.
Read actively: Take notes, reflect on themes, and connect ideas to current world events.
Discuss with others: Sharing perspectives enriches understanding.
Apply insights: Let the ideas inform your personal and professional life.
Telescopes use mirrors or lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects, allowing astronomers to see them: Light collection The size of a telescope's main mirror or lens determines how much light it can collect. Larger mirrors or lenses can collect more light and detect fainter objects. LighRead more
Telescopes use mirrors or lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects, allowing astronomers to see them:
Light collection
The size of a telescope’s main mirror or lens determines how much light it can collect. Larger mirrors or lenses can collect more light and detect fainter objects.
Light focusing
The shape of the mirror or lens concentrates light into a single point, called the focal point.
Image magnification
When viewed through a telescope’s eyepiece or camera, the concentrated image appears magnified.
There are several types of telescopes, including:
Refracting telescopes
Use lenses to bend, or refract, light. The first telescopes were refracting telescopes, and many backyard telescopes today are still refracting.
Reflecting telescopes
Use mirrors to collect and focus light. Reflecting telescopes are ideal for space because large mirrors can be made lighter and thinner than lenses of the same size.
Catadioptric telescopes
Combine lenses and mirrors to focus light. These telescopes are typically compact and easy to transport and handle.
Consider the following statements: ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
Let's analyze the statements: Statement-I: Marsupials are not naturally found in India. This statement is correct. Marsupials, such as kangaroos and koalas, are primarily found in Australia and nearby islands. They are not native to India. Statement-II: Marsupials can thrive only in montane grasslanRead more
Let’s analyze the statements:
Statement-I: Marsupials are not naturally found in India. This statement is correct. Marsupials, such as kangaroos and koalas, are primarily found in Australia and nearby islands. They are not native to India.
Statement-II: Marsupials can thrive only in montane grasslands with no predators. This statement is incorrect. Marsupials inhabit a wide variety of environments, including forests, grasslands, and deserts. They are not limited to montane grasslands and can coexist with predators, as evidenced by their presence in diverse habitats in Australia, where they have adapted to various ecological niches.
Therefore, the correct answer is: Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
See lessIn Java, consider the following code snippet:Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter your age: "); int age = sc.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter your full name: "); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("Age: " + age); System.out.println("Name: " + name);When ...Read more
The nextLine() method appears to skip input because after executing nextInt(), the newline character (\n) from pressing Enter is still left in the input buffer. When nextLine() is called immediately after, it reads this leftover newline character instead of waiting for new user input. As a result, iRead more
The nextLine() method appears to skip input because after executing nextInt(), the newline character (\n) from pressing Enter is still left in the input buffer.
When nextLine() is called immediately after, it reads this leftover newline character instead of waiting for new user input. As a result, it returns an empty string and seems to “skip” the input.
To fix the issue, insert an extra sc.nextLine(); after nextInt() to consume the leftover newline character.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter your age: “);
int age = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // consume the leftover newline
System.out.print(“Enter your full name: “);
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(“Age: ” + age);
System.out.println(“Name: ” + name);
Now, if the input is:
20
Rahul Sharma
The output will be:
Age: 20
Name: Rahul Sharma
What is the difference between chemical and physical weathering?
Comparison of chemical weathering and physical weathering: Aspect Chemical Weathering Physical Weathering Definition The breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions, altering their composition. The mechanical breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces without changing their composition. Process InvolvRead more
Comparison of chemical weathering and physical weathering:
| Aspect | Chemical Weathering | Physical Weathering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions, altering their composition. | The mechanical breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces without changing their composition. |
| Process | Involves chemical reactions such as oxidation, hydrolysis, and carbonation. | Involves physical forces like freezing and thawing, abrasion, and temperature changes. |
| Main Agents | Water, acids, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. | Temperature changes, ice, water, wind, and biological activity. |
| Composition Change | Alters the chemical composition of the rock. | No change in the chemical composition of the rock. |
| Appearance Change | Rocks may dissolve, change color, or form new minerals. | Rocks break into smaller pieces or develop cracks and fractures. |
| Examples | Formation of rust on rocks due to oxidation; limestone dissolving in acid rain. | Frost wedging (freeze-thaw cycles), exfoliation, or root wedging by plants. |
| Location Preference | Common in warm, wet climates where water and acids are abundant. | Common in cold or arid climates where physical forces dominate. |
| Rate of Process | Generally slower but leads to significant long-term changes. | Can be rapid in extreme conditions (e.g., freeze-thaw cycles). |
This comparison highlights the distinct ways in which chemical and physical weathering affect Earth’s surface.
See lessNational Technology Day is celebrated annually on May 11 in India. It marks the anniversary of the Pokhran-II nuclear tests conducted in 1998, showcasing India's technological advancements. The day also highlights the contributions of Indian scientists, engineers, and innovators in the field of techRead more
National Technology Day is celebrated annually on May 11 in India.
It marks the anniversary of the Pokhran-II nuclear tests conducted in 1998, showcasing India’s technological advancements. The day also highlights the contributions of Indian scientists, engineers, and innovators in the field of technology and science.
See lessHow is “Offside” rule applied in rugby?
The offside rule in rugby, both in Rugby Union and Rugby League, is a fundamental aspect that ensures fair play by maintaining the structure of the game. Here’s how it is applied: General Offside in Open Play A player is offside if they are in front of a teammate who last played the ball or carriedRead more
The offside rule in rugby, both in Rugby Union and Rugby League, is a fundamental aspect that ensures fair play by maintaining the structure of the game. Here’s how it is applied:
The offside rule maintains the game’s flow and ensures that players adhere to fair play standards, contributing to rugby’s strategic and structured nature.
See lessWhen was the first airplane invented?
The first successful powered airplane was invented by Wilbur and Orville Wright, commonly known as the Wright Brothers. They achieved the first controlled, sustained flight of a powered, heavier-than-air aircraft on December 17, 1903, near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Their airplane, the Wright FlyerRead more
The first successful powered airplane was invented by Wilbur and Orville Wright, commonly known as the Wright Brothers. They achieved the first controlled, sustained flight of a powered, heavier-than-air aircraft on December 17, 1903, near Kitty Hawk, North Carolina.
Their airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew for 12 seconds and covered 120 feet during its first flight. This marked the beginning of modern aviation.
See lessHow does deforestation impact biodiversity and what are the broader environmental consequences?
Deforestation significantly impacts biodiversity by destroying habitats that are critical for various species. When forests are cleared, many plants, animals, insects, and microorganisms lose their homes, leading to a decline in species richness. This loss of biodiversity disrupts ecosystems and weaRead more
Deforestation significantly impacts biodiversity by destroying habitats that are critical for various species. When forests are cleared, many plants, animals, insects, and microorganisms lose their homes, leading to a decline in species richness. This loss of biodiversity disrupts ecosystems and weakens their resilience, making them more vulnerable to disturbances like climate change, diseases, and natural disasters. Deforestation also contributes to soil erosion, reduces the land’s ability to store carbon, and increases greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating global warming. The broader environmental consequences include altered rainfall patterns, decreased soil fertility, and a loss of ecosystem services like water filtration and air purification, which are vital for human survival.
See lessWhat is the function of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system plays a critical role in the process of breathing and gas exchange in the human body. Its primary function is to supply oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, from the body. The respiratory system ensures that oxygen is delivered to the bRead more
The respiratory system plays a critical role in the process of breathing and gas exchange in the human body. Its primary function is to supply oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide, a waste product of metabolism, from the body. The respiratory system ensures that oxygen is delivered to the body’s cells, which is essential for cellular respiration, a process that produces energy for the body’s functions.
The respiratory system consists of several key structures, each playing a role in the process of gas exchange and air movement:
The respiratory system’s primary functions are to facilitate the intake of oxygen, expel carbon dioxide, regulate blood pH, protect the body from harmful particles, produce sound, and assist in temperature regulation. Through these processes, the respiratory system is essential for maintaining homeostasis and providing the body with the oxygen it needs for energy production and cellular functions
See lessWhat is Green Taxonomy?
Green Taxonomy is a classification system that defines which economic activities are environmentally sustainable. It serves as a guideline for businesses, investors, and policymakers to direct capital towards projects and industries that contribute to environmental goals such as climate change mitigRead more
Green Taxonomy is a classification system that defines which economic activities are environmentally sustainable. It serves as a guideline for businesses, investors, and policymakers to direct capital towards projects and industries that contribute to environmental goals such as climate change mitigation, pollution reduction, and biodiversity conservation.
Green taxonomies are a crucial tool in achieving a sustainable and low-carbon economy by directing capital towards projects that genuinely benefit the environment.
See lessHow does the immune system protect the body from disease?
The immune system protects the body from disease by identifying, neutralizing, and eliminating harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. It also detects and removes damaged or abnormal cells, including cancerous cells. Here’s how it works: 1. First Line of Defense: Physical andRead more
The immune system protects the body from disease by identifying, neutralizing, and eliminating harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. It also detects and removes damaged or abnormal cells, including cancerous cells. Here’s how it works:
By working through these layers of defense, the immune system protects the body from infections and promotes overall health.
See lessFind the missing term in the series 3, 9, 27, 81, ?, 729
What skill have you always wanted to learn and why?
I've always wanted to learn playing a musical instrument, like the piano or guitar. Music is a universal language that transcends words and emotions, and the ability to create it feels almost magical. It would not only be a creative outlet but also a way to unwind and express myself in a way that woRead more
I’ve always wanted to learn playing a musical instrument, like the piano or guitar. Music is a universal language that transcends words and emotions, and the ability to create it feels almost magical. It would not only be a creative outlet but also a way to unwind and express myself in a way that words sometimes cannot. Additionally, learning music sharpens the mind, improves focus, and fosters discipline—skills beneficial in all areas of life.
See lessHow do Tibetan Buddhism and Theravada Buddhism differ in their practices?
What is Nitrogen Narcosis?
How does the “mixture of experts” technique contribute to DeepSeek-R1’s efficiency?
The "mixture of experts" (MoE) technique significantly enhances DeepSeek-R1's efficiency through several innovative mechanisms that optimize resource utilization and improve performance. Here’s how this architecture contributes to the model's overall effectiveness: Selective Activation of Experts: DRead more
The “mixture of experts” (MoE) technique significantly enhances DeepSeek-R1’s efficiency through several innovative mechanisms that optimize resource utilization and improve performance. Here’s how this architecture contributes to the model’s overall effectiveness:
The “mixture of experts” technique is central to DeepSeek-R1’s design, allowing it to achieve remarkable efficiency and performance in handling complex AI tasks. By leveraging selective activation, specialization, intelligent routing through gating networks, and effective load balancing, DeepSeek-R1 not only reduces computational costs but also enhances its ability to deliver precise and contextually relevant outputs across various domains. This innovative architecture positions DeepSeek-R1 as a competitive player in the AI landscape, challenging established models with its advanced capabilities.
See lessIndia’s upcoming census (by March 2027) will include caste for the first time since 1951. Will this help improve social justice and policy targeting, or risk reinforcing caste divisions?
India’s decision to include caste enumeration in the upcoming national census marks a significant policy shift with far-reaching social and political implications. Whether this step advances social justice and improves policy targeting or risks reinforcing caste divisions depends largely on its inteRead more
India’s decision to include caste enumeration in the upcoming national census marks a significant policy shift with far-reaching social and political implications. Whether this step advances social justice and improves policy targeting or risks reinforcing caste divisions depends largely on its intent, design, and subsequent use.
On the positive side, comprehensive caste data can strengthen evidence-based policymaking. India’s welfare and affirmative action frameworks are deeply intertwined with caste realities, yet they currently rely on outdated or estimated figures. Accurate and up-to-date data can help identify persistent socio-economic disparities, enable more precise targeting of welfare schemes, and ensure that benefits reach genuinely disadvantaged groups. It may also support more informed debates on reservations, resource allocation, and inclusive development, thereby enhancing transparency and accountability in governance.
Furthermore, caste enumeration can help policymakers recognise intra-group inequalities that often remain invisible under broad social categories. By integrating caste data with indicators such as education, employment, health, and income, the state can design interventions that are more responsive to actual conditions rather than assumptions.
However, the exercise also carries notable risks. Critics argue that officially enumerating caste may reinforce social identities that India has long sought to transcend. There is concern that such data could be politicised, encouraging competitive identity-based mobilisation rather than fostering a shared developmental agenda. If misused, caste statistics could deepen social polarisation and entrench divisions instead of addressing structural inequalities.
There are also practical and ethical challenges related to data accuracy, classification, and privacy. Ensuring uniform self-identification, preventing misreporting, and safeguarding sensitive information will be essential to maintain public trust in the census process.
In conclusion, caste enumeration in the census is neither inherently progressive nor inherently divisive. Its impact will depend on how responsibly the data is collected, interpreted, and applied. If used as a tool for inclusive, evidence-based policymaking with strong safeguards against political misuse, it can advance social justice. If handled poorly, it risks reinforcing the very hierarchies it seeks to address. The challenge, therefore, lies not in the data itself, but in the governance framework that surrounds it.
See lessWhy does it rain in winter?
Rainfall in the winter in India is caused by western disturbances, which are low-pressure systems that originate in the Mediterranean Sea and move east across the globe: How they form Western disturbances are extratropical storms that form over the Mediterranean Sea, Caspian Sea, and Black Sea. HowRead more
Rainfall in the winter in India is caused by western disturbances, which are low-pressure systems that originate in the Mediterranean Sea and move east across the globe:
How they form
Western disturbances are extratropical storms that form over the Mediterranean Sea, Caspian Sea, and Black Sea.
How they reach India
The westerly jetstream steers the western disturbances east towards India.
How they cause rainfall
When the western disturbances reach the Indian subcontinent, they get blocked by the Himalayas and cause rain in the northwest plains and snow in the higher altitudes of the Western Himalayas.
How they affect the weather
Western disturbances can cause moderate to heavy rain in low-lying areas and heavy snow in mountainous areas. They can also cause unusual rainfall, increased temperatures during nights, and cloudy skies.
How they affect the crops
Western disturbances are important for the growth of wheat in Punjab and Haryana. However, excessive rainfall can also damage crops, cause floods, and avalanches.
How they affect the fog
Winter rain increases the humidity in the air, which can make fog more dense.
How does the water cycle work in nature?
The water cycle shows the continuous movement of water within the Earth and atmosphere. It is a complex system that includes many different processes. Liquid water evaporates into water vapor, condenses to form clouds, and precipitates back to earth in the form of rain and snow
The water cycle shows the continuous movement of water within the Earth and atmosphere. It is a complex system that includes many different processes. Liquid water evaporates into water vapor, condenses to form clouds, and precipitates back to earth in the form of rain and snow
See lesshow did the mesopotamian civilization end?
The Mesopotamian civilization, often regarded as one of the cradles of civilization, didn't end abruptly but gradually declined due to a combination of factors over several centuries. Here's an overview of the key reasons for its decline: 1. Environmental Changes: The region suffered from environmenRead more
The Mesopotamian civilization, often regarded as one of the cradles of civilization, didn’t end abruptly but gradually declined due to a combination of factors over several centuries. Here’s an overview of the key reasons for its decline:
1. Environmental Changes: The region suffered from environmental degradation, including soil salinization and deforestation, which reduced agricultural productivity. Over time, this led to food shortages and weakened the economic foundation of Mesopotamian societies.
2. Invasions and Conquests: The Mesopotamian city-states were frequently invaded by outside forces. Key conquests included:
The Akkadian Empire (c. 2334–2154 BCE) was the first to unify the region but eventually collapsed due to internal strife and invasions.
The Babylonian Empire, under Hammurabi, rose and fell due to invasions, particularly by the Hittites and later the Kassites.
The Assyrian Empire (c. 900–612 BCE) eventually fell to a coalition of Medes, Babylonians, and Scythians, who sacked the Assyrian capital, Nineveh, in 612 BCE.
The Neo-Babylonian Empire (c. 626–539 BCE) flourished briefly under leaders like Nebuchadnezzar II but fell to the Persian Empire led by Cyrus the Great in 539 BCE.
3. Political Instability: Continuous power struggles, both internal and external, weakened the states. Shifting alliances and frequent wars drained resources and destabilized the region.
4. Economic Decline: The constant state of war and the burden of maintaining large armies and infrastructure projects strained the economy. Trade routes were disrupted, further exacerbating economic issues.
5. Cultural Assimilation: After the conquest by the Persian Empire, Mesopotamian culture began to merge with Persian culture. Although some Mesopotamian traditions persisted, the distinct identity of the civilization faded over time.
Eventually, the rise of new powers and cultures in the region, such as the Greeks under Alexander the Great and later the Romans, further assimilated and replaced the remaining elements of Mesopotamian culture.
These factors collectively led to the gradual decline of Mesopotamian civilization, marking the end of its dominance in the ancient world.
See lessWhat Are the Benefits of Asset Tracking Solutions for Businesses in Australia?
Asset tracking solutions are invaluable for businesses across Australia that manage valuable equipment or inventory. Using asset tracking solutions enables companies to monitor their assets’ locations in real-time, which helps prevent loss, theft, and misplacement. This is especially beneficial in sRead more
Asset tracking solutions are invaluable for businesses across Australia that manage valuable equipment or inventory. Using asset tracking solutions enables companies to monitor their assets’ locations in real-time, which helps prevent loss, theft, and misplacement. This is especially beneficial in sectors such as construction, logistics, and manufacturing, where assets often move across various locations.
By implementing asset tracking solutions, businesses can increase operational efficiency by ensuring equipment is where it’s needed when it’s needed. This visibility improves workflow and productivity, as assets are better allocated and less time is wasted searching for misplaced items.
Another key benefit of asset tracking solutions is the ability to maintain assets more effectively. These systems often include alerts for scheduled maintenance or potential performance issues, preventing costly downtime and extending the lifespan of critical equipment.
In addition, asset tracking solutions enhance security. By setting up geofencing, companies can receive instant alerts if an asset leaves a designated area, allowing for quick action. Overall, asset tracking solutions offer Australian businesses improved security, productivity, and asset management, making them essential for protecting valuable resources and maintaining seamless operations.
For more information, please visit: https://www.netcorp.com.au/
See lessWhat causes the seasons on Earth?
The seasons on Earth are caused by the tilt of Earth's axis and its orbit around the Sun. Here's how these factors contribute: Tilt of Earth's Axis: Earth's axis is tilted at an angle of about 23.5 degrees relative to its orbit around the Sun. This tilt means that different parts of Earth receive vaRead more
The seasons on Earth are caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis and its orbit around the Sun. Here’s how these factors contribute:
The Earth’s axial tilt causes the variation in sunlight during the year, which, in turn, causes the changing seasons.
See lessWhat is the theory of relativity?
The theory of relativity, developed by Albert Einstein in the early 20th century, revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity. It consists of two main parts: special relativity and general relativity. Special Relativity (1905) This theory deals with the physics of objects moving atRead more
The theory of relativity, developed by Albert Einstein in the early 20th century, revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity. It consists of two main parts: special relativity and general relativity.
This theory deals with the physics of objects moving at constant speeds, particularly those approaching the speed of light. Its core concepts include:
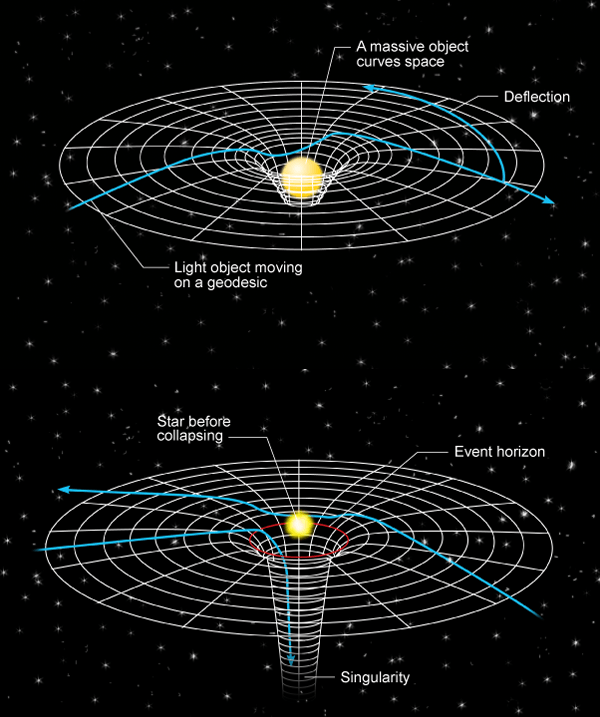
Source: Physics Magazine
Key consequences of special relativity:
This theory extends special relativity to include acceleration and introduces a new understanding of gravity. Its core ideas are:
Key consequences of general relativity:
Einstein’s theories have been confirmed through numerous experiments and observations, such as the bending of light by gravity and the precise timekeeping of GPS satellites, which must account for both special and general relativity effects. These theories form the foundation of modern physics, especially in understanding the cosmos, from black holes to the expansion of the universe.
See lessWhat were the different types Dinosaurs present on the earth?
Dinosaurs were incredibly diverse and can be categorized into various types based on their physical characteristics, diet, and evolutionary lineage. Here's an overview of the main types of dinosaurs: Theropods Diet: Carnivorous (meat-eating). Characteristics: Bipedal, with sharp teeth and claws. ExaRead more
Dinosaurs were incredibly diverse and can be categorized into various types based on their physical characteristics, diet, and evolutionary lineage. Here’s an overview of the main types of dinosaurs:
These types highlight the incredible variety among dinosaurs, showcasing their adaptations to different environments and niches during the Mesozoic Era.
See lessHow does the law of inertia work?
The law of inertia, also known as Newton's First Law of Motion, states that an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line at a constant speed unless acted upon by an external force. This law highlights the concept that objects tend to maintain their current state of motion. Key Points ofRead more
The law of inertia, also known as Newton’s First Law of Motion, states that an object will remain at rest or move in a straight line at a constant speed unless acted upon by an external force. This law highlights the concept that objects tend to maintain their current state of motion.
The law of inertia explains why no force is needed to keep an object moving at a constant velocity and why forces are required to change the motion of objects.
See less
Introduction: The Eternal Hymn of Detachment and Devotion Shiv Rudrashtakam is one of the most profound Sanskrit hymns dedicated to Lord Shiva, the supreme yogi, destroyer of ignorance, and embodiment of pure consciousness. Composed by Adi Shankaracharya, this eight-verse stotra ...

A Prime-Adam Number is defined as a positive number that fulfills two conditions simultaneously: it is a prime number and also an Adam number. For example, take the number 13; its reverse is 31. The square of 13 is 169, and the ...

Introduction The 74th Miss Universe pageant, held on November 21, 2025, at the Impact Challenger Hall in Nonthaburi, Thailand, set a new benchmark in global beauty contests. Not merely a showcase of beauty and fashion, this year’s event stood as ...

A Keith number is an n-digit number that appears as a term in a sequence, where the first n terms are its own digits, and each following term is the sum of the previous n terms. For example, 197 is ...

A matrix is called Doubly Markov if it satisfies the following conditions: All elements are greater than or equal to 0. The sum of each row is equal to 1. The sum of each column is equal to 1. The program should ...

The Dawn of a Clean Energy Revolution Imagine a world where air pollution is history, industries run clean, and the very fuel that powers our lives leaves nothing behind but water vapor. Sounds like science fiction? It’s the promise of ...
Sterilization refers to actions taken by the central bank (in this case, the Reserve Bank of India) to manage the impact of foreign capital flows on the domestic money supply. Open Market Operations (OMOs) are one such tool where the central bank buys or sells government securities in the open markeRead more
Sterilization refers to actions taken by the central bank (in this case, the Reserve Bank of India) to manage the impact of foreign capital flows on the domestic money supply. Open Market Operations (OMOs) are one such tool where the central bank buys or sells government securities in the open market to influence liquidity and control inflation or currency appreciation/depreciation. This process helps in managing the domestic monetary base without affecting other macroeconomic variables. Therefore, the correct answer is Conducting ‘Open Market Operations’.
See less