The Indus Valley Civilization is believed to have been primarily centered in which present-day country?
Poll Results
Please login to vote and see the results.
Sign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
At Qukut, our mission is to bridge the gap between knowledge seekers and knowledge sharers. We strive to unite diverse perspectives, fostering understanding and empowering everyone to contribute their expertise. Join us in building a community where knowledge flows freely and growth is limitless.
The Indus Valley Civilization is believed to have been primarily centered in which present-day country?
Please login to vote and see the results.
The term ‘Swadeshi Movement’ was first coined by?
Please login to vote and see the results.
Which of the following was the first country to develop nuclear weapons?
Please login to vote and see the results.
How does the “mixture of experts” technique contribute to DeepSeek-R1’s efficiency?
What specific challenges did DeepSeek-R1-Zero face during its development ?
How does the “chain-of-thought” reasoning improve the accuracy of DeepSeek-R1 ?
What is DeepSeek R1?
DeepSeek R1 is an advanced AI language model developed by the Chinese startup DeepSeek. It is designed to enhance problem-solving and analytical capabilities, demonstrating performance comparable to leading models like OpenAI's GPT-4. Key Features: Reinforcement Learning Approach: DeepSeek R1 employRead more
DeepSeek R1 is an advanced AI language model developed by the Chinese startup DeepSeek. It is designed to enhance problem-solving and analytical capabilities, demonstrating performance comparable to leading models like OpenAI’s GPT-4. Key Features:
Performance Highlights:
Accessing DeepSeek R1:
DeepSeek R1 represents a significant advancement in AI language models, combining innovative training methods with open-source accessibility and cost-effectiveness.
See lessWhat is empty nest syndrome? How to cope with ENS?
Empty Nest Syndrome (ENS) is a psychological condition characterized by feelings of sadness, loneliness, or loss experienced by parents or caregivers when their children leave home, usually for reasons such as going to college, getting married, or moving out for work. Although it is not a clinicallyRead more
Empty Nest Syndrome (ENS) is a psychological condition characterized by feelings of sadness, loneliness, or loss experienced by parents or caregivers when their children leave home, usually for reasons such as going to college, getting married, or moving out for work. Although it is not a clinically diagnosed mental health condition, it can have a significant emotional impact.
Key Symptoms of ENS:
Sadness and Loneliness: A profound sense of emptiness and isolation.
Loss of Purpose: Feeling as if life has lost meaning after children leave.
Depression or Anxiety: Persistent feelings of unhappiness or worry.
Identity Crisis: Struggling to adapt to a new identity beyond being a caregiver.
How to Cope with Empty Nest Syndrome
Coping with ENS involves emotional adjustment and finding new ways to create purpose and joy in life. Here are practical strategies:
1. Reframe Your Perspective
View your child’s independence as a positive milestone in their growth.
Celebrate their achievements and focus on the successful role you played in shaping their future.
2. Rediscover Your Identity
Reconnect with personal passions or hobbies that were set aside during parenting years.
Explore activities such as painting, writing, gardening, or traveling.
3. Strengthen Relationships
Focus on nurturing your relationship with your partner or spouse.
Spend quality time with friends or build new social connections.
4. Pursue New Goals
Take up a new skill, enroll in a course, or volunteer in your community.
Revisit career aspirations or start a new project.
5. Stay Connected with Your Children
Maintain regular communication, but respect their independence.
Use technology like video calls, messaging, or emails to stay in touch.
6. Practice Self-Care
Focus on physical and mental well-being through exercise, healthy eating, and mindfulness practices.
Consider meditation, yoga, or therapy to manage stress or overwhelming emotions.
7. Seek Support
Talk to friends, family, or support groups who understand what you’re going through.
Consider speaking with a therapist if ENS leads to prolonged depression or anxiety.
8. Embrace the Opportunity
Use this phase as an opportunity to travel, explore new cultures, or build experiences that enrich your life.
By focusing on personal growth and maintaining positive connections, parents can successfully navigate this transitional phase and find fulfillment beyond their caregiving role.
See lessThe word ‘Denisovan’ is sometimes mentioned in media in reference to?
The word Denisovan refers to an extinct group of archaic humans that lived in parts of Asia around 50,000 to 200,000 years ago. They are named after the Denisova Cave in Siberia, where their fossils and genetic material were first discovered in 2008. Denisovans are closely related to Neanderthals anRead more
The word Denisovan refers to an extinct group of archaic humans that lived in parts of Asia around 50,000 to 200,000 years ago. They are named after the Denisova Cave in Siberia, where their fossils and genetic material were first discovered in 2008. Denisovans are closely related to Neanderthals and modern humans, and their DNA has been found in some modern populations, particularly among Melanesians, Aboriginal Australians, and some Southeast Asian groups.
In media, the term is often mentioned in discussions about human evolution, genetics, and the interbreeding between different human species in ancient times.
See lessHow did the planets in our solar system get their names?
The names of the planets in our solar system are rooted in ancient mythology and cultural traditions. Here’s a breakdown: Mercury: Named after the Roman messenger god, Mercury, known for his speed, because the planet moves quickly across the sky. Venus: Named after the Roman goddess of love and beauRead more
The names of the planets in our solar system are rooted in ancient mythology and cultural traditions. Here’s a breakdown:
The tradition of naming planets after Roman and Greek gods reflects the influence of ancient astronomers, who sought to connect celestial objects with divine figures from their mythologies. This convention continues today for newly discovered celestial bodies.
See lessWhich ruler has built Sanchi Stupa ?
Please login to vote and see the results.
what are trade tarriffs and how do they work?
Trade tariffs are taxes or duties imposed by a government on goods and services imported from other countries. They are a common tool in international trade policy and serve various economic and political purposes. Here's a detailed breakdown of what tariffs are and how they work: Types of Tariffs ARead more
Trade tariffs are taxes or duties imposed by a government on goods and services imported from other countries. They are a common tool in international trade policy and serve various economic and political purposes. Here’s a detailed breakdown of what tariffs are and how they work:
Trade tariffs are a powerful but often controversial tool in economic policy. While they can protect domestic industries and generate revenue, they may also lead to higher consumer costs and strained international relations.
See lesswhich generation can possibly provide psychoeducation to others about the use of technology? a. generation z b. generation y c. generation x d. baby boomers
What is the continental drift theory??
The Continental Drift Theory is a geological hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912. It suggests that the Earth's continents were once part of a single, massive supercontinent called Pangaea, which began to break apart approximately 200 million years ago. Over time, the fragments drifted to tRead more
The Continental Drift Theory is a geological hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912. It suggests that the Earth’s continents were once part of a single, massive supercontinent called Pangaea, which began to break apart approximately 200 million years ago. Over time, the fragments drifted to their current positions on the Earth’s surface.
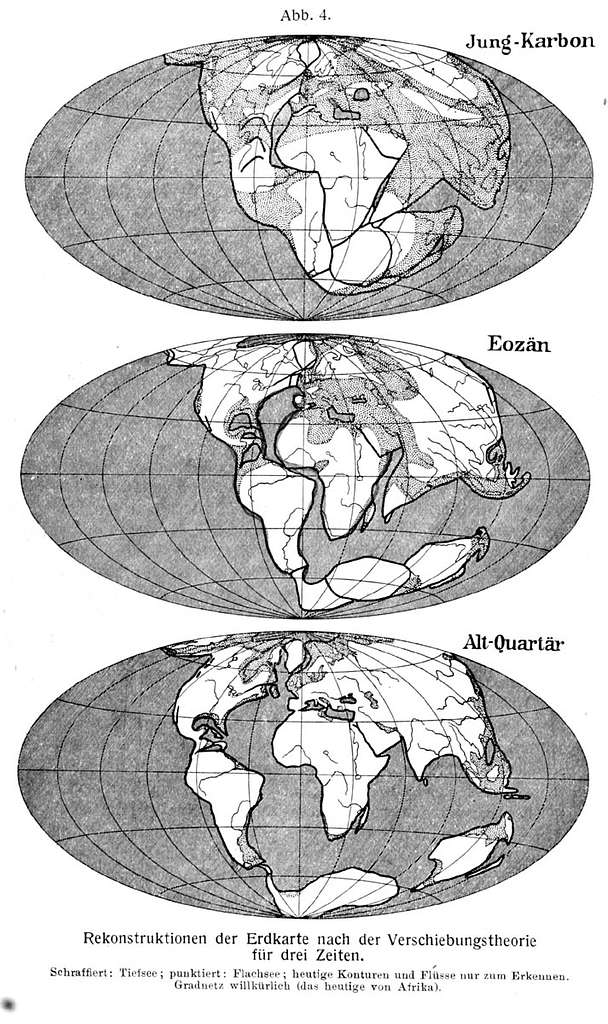
Source: Cambridge University Press
In essence, the Continental Drift Theory was a groundbreaking idea that transformed geology and paved the way for our current understanding of Earth’s structure and the movement of its continents.
See lessWhat are the basic rules of badminton for doubles play?
Badminton doubles play follows the same general rules as singles but includes unique aspects tailored for a two-player team on each side. Here are the basic rules of badminton doubles play: Court Dimensions and Boundaries Court Size: The doubles court is wider than the singles court. The boundariesRead more
Badminton doubles play follows the same general rules as singles but includes unique aspects tailored for a two-player team on each side. Here are the basic rules of badminton doubles play:
By adhering to these rules, doubles play becomes a dynamic and strategic game that tests teamwork, reflexes, and coordination!
See lessWhat are the main teachings of Confucianism?
Confucianism, rooted in the teachings of Confucius (551–479 BCE), is a philosophical and ethical system that emphasizes personal development, societal harmony, and moral integrity. Below are its main teachings: Ren (Humaneness or Benevolence) Core Idea: The concept of Ren emphasizes compassion, empaRead more
Confucianism, rooted in the teachings of Confucius (551–479 BCE), is a philosophical and ethical system that emphasizes personal development, societal harmony, and moral integrity. Below are its main teachings:
Confucianism focuses on improving individual character to create a just and harmonious society. Its teachings remain relevant and influential in ethics, governance, and interpersonal relationships worldwide.
See lessWhich ruler has won Malwa, Gujarat and Maharashtra for the first time?
Please login to vote and see the results.
Which one of the following is the initial branch of Indian Philosophy?
Please login to vote and see the results.
The word Satyamev Jayate has been taken from:
Please login to vote and see the results.
What is Kinetic Energy?
Kinetic Energy is the energy that an object possesses due to its motion. It is a type of mechanical energy and depends on two factors: the mass of the object and the velocity (speed) at which it is moving. The mathematical formula for kinetic energy (KEKE) is: K.E = $\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}$ where: mm isRead more
Kinetic Energy is the energy that an object possesses due to its motion. It is a type of mechanical energy and depends on two factors: the mass of the object and the velocity (speed) at which it is moving. The mathematical formula for kinetic energy () is:
K.E = $\frac{1}{2}mv^{2}$
where:
Who is Himani Mor?
Himani Mor is a notable Indian tennis player and the wife of Olympic javelin champion Neeraj Chopra. Here’s a concise overview of her life and career: Born on June 26, 1999, in Larsauli village, Sonipat, Haryana, Himani was encouraged to pursue tennis from a young age. She attended Little Angels SchRead more
Himani Mor is a notable Indian tennis player and the wife of Olympic javelin champion Neeraj Chopra. Here’s a concise overview of her life and career:
Born on June 26, 1999, in Larsauli village, Sonipat, Haryana, Himani was encouraged to pursue tennis from a young age. She attended Little Angels School and later studied Political Science and Physical Education at Miranda House, Delhi University. She furthered her education in Sports Management at Franklin Pierce University in the United States.
Himani has made significant contributions to Indian tennis, achieving rankings of 42nd in singles and 27th in doubles according to the All India Tennis Association (AITA). Her competitive journey includes participation in various national and international tournaments.
In addition to her playing career, she has taken on coaching roles. Himani served as a Volunteer Assistant Tennis Coach at Franklin Pierce University and is currently a Graduate Assistant at Amherst College, where she manages the women’s tennis team.
Himani gained media attention after marrying Neeraj Chopra on January 18, 2025. Their relationship symbolizes a union of two celebrated athletes, attracting significant public interest.
At just 25 years old, Himani Mor exemplifies dedication in both sports and academics. Her journey inspires many young athletes, particularly women, as she balances her professional aspirations with her new role as a supportive partner to Neeraj Chopra.
See lessWhat are the different types of strokes used in competitive swimming?
Stroke Technique Breathing Event Distances Freestyle (Front Crawl) Arms alternate in a windmill motion; legs perform a flutter kick. Turn head to the side to breathe every 2-4 strokes. 50m, 100m, 200m, 400m, 800m, 1500m; relays. Backstroke Arms alternate in a circular motion; legs perform a fRead more
| Stroke | Technique | Breathing | Event Distances |
|---|---|---|---|
| Freestyle (Front Crawl) | Arms alternate in a windmill motion; legs perform a flutter kick. | Turn head to the side to breathe every 2-4 strokes. | 50m, 100m, 200m, 400m, 800m, 1500m; relays. |
| Backstroke | Arms alternate in a circular motion; legs perform a flutter kick while lying on the back. | Face is above water, making breathing easier. | 50m, 100m, 200m. |
| Breaststroke | Both arms move simultaneously in a half-circle; legs perform a frog kick. | Head lifts above water to breathe with each stroke. | 50m, 100m, 200m. |
| Butterfly | Both arms move simultaneously overhead; legs perform a dolphin kick. | Head and chest lift out of water to breathe every 1-2 strokes. | 50m, 100m, 200m. |
| Individual Medley (IM) | Uses all four strokes in order: butterfly, backstroke, breaststroke, freestyle. | Varies by stroke; each stroke’s breathing technique is followed. | 100m (short-course), 200m, 400m. |
| Freestyle Relay | Teams of four swim equal distances in freestyle. | Turn head to breathe, as in freestyle. | 4x100m, 4x200m. |
| Medley Relay | Teams of four swim in order: backstroke, breaststroke, butterfly, freestyle. | Breathing varies by stroke. | 4x100m. |
How is “Offside” rule applied in rugby?
The offside rule in rugby, both in Rugby Union and Rugby League, is a fundamental aspect that ensures fair play by maintaining the structure of the game. Here’s how it is applied: General Offside in Open Play A player is offside if they are in front of a teammate who last played the ball or carriedRead more
The offside rule in rugby, both in Rugby Union and Rugby League, is a fundamental aspect that ensures fair play by maintaining the structure of the game. Here’s how it is applied:
The offside rule maintains the game’s flow and ensures that players adhere to fair play standards, contributing to rugby’s strategic and structured nature.
See lessWhat are the key rituals and practices of Shinto?
Shinto, the indigenous religion of Japan, is characterized by rituals and practices that focus on reverence for nature, ancestors, and kami (spiritual beings or deities). Here are the key rituals and practices: Kami Worship Shrines (Jinja): Shinto shrines are the physical spaces where kami are enshrRead more
Shinto, the indigenous religion of Japan, is characterized by rituals and practices that focus on reverence for nature, ancestors, and kami (spiritual beings or deities). Here are the key rituals and practices:
These practices emphasize purity, respect for nature, and the deep connection between humans and the spiritual realm, forming the foundation of Shinto beliefs.
See lessExplain the 3 classes of levers
Lever is the force placed between the fulcrum and the load. If the load is closer to the fulcrum, researchers of movement in the load require less force. If the force is closer to the fulcrum, movement of the load requires more force.
Lever is the force placed between the fulcrum and the load. If the load is closer to the fulcrum, researchers of movement in the load require less force. If the force is closer to the fulcrum, movement of the load requires more force.
See lessHow does altitude affect endurance in long-distance running?
Altitude significantly affects endurance in long-distance running due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Here's a detailed breakdown of how altitude impacts performance: Reduced Oxygen Availability At higher altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is lower, which leads to a decrease in the partial pRead more
Altitude significantly affects endurance in long-distance running due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how altitude impacts performance:
Altitude poses a challenge to endurance in long-distance running by limiting oxygen availability, but with proper acclimatization, athletes can adapt and potentially gain a competitive edge when returning to lower altitudes.
See lessWhat is the role of the Pope in the Catholic Church?
The Pope holds a pivotal role in the Catholic Church, serving as the spiritual leader and the highest authority within the Church. Here are the key aspects of the Pope's role: Spiritual Leader Supreme Pontiff: The Pope is regarded as the supreme spiritual leader of Catholics worldwide, guiding the CRead more
The Pope holds a pivotal role in the Catholic Church, serving as the spiritual leader and the highest authority within the Church. Here are the key aspects of the Pope’s role:
Through these roles, the Pope ensures the Church remains steadfast in its mission, adapting to changing times while preserving its core teachings.
See lessHow does the adminstration done on the Public during the Gupta period
During the Gupta period (approximately 320 to 550 CE), administration was characterized by a highly organized and efficient system that contributed to the prosperity and stability of the empire. Here are the main aspects of how administration was conducted: 1. Central Administration Monarchical SystRead more
During the Gupta period (approximately 320 to 550 CE), administration was characterized by a highly organized and efficient system that contributed to the prosperity and stability of the empire. Here are the main aspects of how administration was conducted:
1. Central Administration
Monarchical System: The Gupta Empire was ruled by a king, often considered divine or semi-divine, who held supreme authority. The king was the central figure in governance, with ultimate control over the military, judiciary, and administrative functions.
Council of Ministers: The king was assisted by a council of ministers (Mantriparishad), who advised on various matters of state. These ministers were often from noble families or scholars well-versed in administrative affairs.
2. Provincial Administration
Division into Provinces: The empire was divided into provinces (Bhukti), each governed by a provincial governor (Uparika), who acted as the king’s representative.
Viceroys: Often, members of the royal family were appointed as viceroys to ensure loyalty and effective governance in these provinces.
Districts and Villages: Provinces were further divided into districts (Vishaya), governed by district officers (Vishayapati). These districts comprised multiple villages, which were the smallest administrative units.
3. Local Administration
Village Autonomy: Villages had a considerable degree of autonomy, with village councils (Grama Sabha) managing local affairs, including the collection of taxes and maintenance of law and order. These councils included elders and local leaders who were respected members of the community.
Tax Collection: Villages were responsible for collecting taxes, which were then forwarded to the district authorities. Taxes were often paid in kind, such as grains, cattle, or produce.
4. Judicial Administration
King as Chief Justice: The king was the highest judicial authority, with the power to pass final judgments. However, local disputes were typically resolved by village assemblies or district courts.
Dharma and Smriti: The judicial system was based on Dharma (moral law) and Smriti (legal texts), which were interpretations of ancient scriptures and customs.
Role of Officials: Officers like Mahadandanayaka (chief judicial officer) and Amatya (minister) played significant roles in judicial matters.
5. Military Administration
Standing Army: The Gupta Empire maintained a well-organized standing army to protect the empire and expand its territories. The military included infantry, cavalry, chariots, and elephants.
Feudal Lords: Local chiefs and feudal lords often provided additional military support in exchange for land grants or other privileges.
6. Revenue Administration
Land Revenue: The primary source of revenue was land tax, which was usually a share of the produce. The rate could vary depending on the fertility of the land and local customs.
Other Taxes: In addition to land revenue, taxes were collected on trade, irrigation, and professional services. Merchants and artisans contributed to the state’s income through these levies.
7. Economic and Trade Administration
Flourishing Trade: The Gupta period saw significant trade, both inland and overseas, which was facilitated by efficient road networks and ports.
Regulation: Trade and commerce were regulated to ensure the prosperity of the empire. Guilds played a crucial role in economic administration, managing the production and trade of goods.
The Gupta administration was a blend of centralization and decentralization, ensuring both control and flexibility, which contributed to the overall stability and prosperity of the empire during its golden age.
See lessWhat are the main techniques used in figure skating routines?
Figure skating routines incorporate a variety of technical elements that showcase a skater's skill, artistry, and athleticism. The main techniques used in figure skating routines include: 1. Jumps Axel Jump: This is the only jump that takes off from a forward edge. It requires an extra half rotationRead more
Figure skating routines incorporate a variety of technical elements that showcase a skater’s skill, artistry, and athleticism. The main techniques used in figure skating routines include:
1. Jumps
Axel Jump: This is the only jump that takes off from a forward edge. It requires an extra half rotation, making it one of the most challenging jumps.
Toe Jumps: These include the Toe Loop, Flip, and Lutz. They start with a toe pick on the ice for takeoff.
Edge Jumps: These include the Salchow and Loop jumps, which take off from the edge of the skate without the use of the toe pick.
Combinations: Skaters often perform combinations of jumps in quick succession to increase the routine’s difficulty and earn more points.
2. Spins
Upright Spin: A basic spin where the skater remains upright.
Sit Spin: The skater’s body is low to the ice, with one leg extended forward.
Camel Spin: The skater extends one leg behind while spinning, maintaining a parallel position to the ice.
Flying Spins: Spins that involve a jump into the spinning position, adding complexity.
3. Footwork Sequences
Steps and Turns: Skaters perform intricate patterns on the ice using various steps like mohawks, choctaws, and rockers, as well as turns such as three-turns and brackets.
Edge Work: Precision in using the inside and outside edges of the blades is crucial for control and fluidity.
4. Lifts (in Pairs Skating)
Overhead Lifts: The male partner lifts the female partner above his head while skating.
Twist Lifts: The female partner is thrown into the air, performs twists, and is caught by her partner.
Death Spiral: The male partner holds the female partner’s hand while she circles around him close to the ice in a deep lean.
5. Choreographic Elements
Transitions: Movements that link jumps, spins, and other elements, enhancing the flow and artistry of the routine.
Interpretation: Skaters express the music’s character and rhythm through their movements and expressions, adding an emotional dimension to the performance.
6. Pairs and Ice Dance Techniques
Synchronization: In pairs skating and ice dance, partners must perform in perfect harmony.
Lifts and Throws (Pairs): Throws involve the male partner launching the female partner into a jump, adding complexity to the performance.
Dance Spins and Lifts (Ice Dance): These are less about height and more about grace and form, following specific rules to maintain the dance essence.
These techniques, combined with artistic expression, make figure skating a captivating blend of sport and art.
See lessHow does the Tao Te Ching influence Taoism?
The Tao Te Ching, attributed to Laozi (Lao Tzu) and composed around the 6th century BCE, is not just a foundational text of Taoism — it is its philosophical heartbeat. Its 81 short chapters, written in poetic verse, provide a cryptic yet profound vision of how to live in harmony with the Tao, or "ThRead more
The Tao Te Ching, attributed to Laozi (Lao Tzu) and composed around the 6th century BCE, is not just a foundational text of Taoism — it is its philosophical heartbeat. Its 81 short chapters, written in poetic verse, provide a cryptic yet profound vision of how to live in harmony with the Tao, or “The Way.”
Below is a deep and structured exploration of how the Tao Te Ching shapes Taoism — culturally, spiritually, ethically, and philosophically.
The Tao Te Ching is the first and most influential source that attempts to articulate what the Tao is:
“The Tao that can be told is not the eternal Tao.”
This sets the tone for Taoism’s central idea:
The Tao is an unseen, unnameable force that underlies all existence.
It is not a god or a doctrine, but a natural flow — the way things are.
In Taoist practice, this inspires:
Non-interference (wu wei)
Simplicity and naturalness (ziran)
Respect for cycles, change, and paradox
The Tao Te Ching becomes a lens through which reality is interpreted — not controlled.
One of the most revolutionary teachings of the Tao Te Ching is wu wei, often misunderstood as laziness or passivity.
“The sage does nothing, yet nothing is left undone.”
Wu wei means:
Acting in alignment with the Tao — effortlessly and spontaneously.
Avoiding forced actions that go against nature.
Trusting the rhythm of life rather than imposing will upon it.
In Taoist lifestyle, this becomes:
Letting go of overthinking.
Allowing relationships, creativity, and decisions to unfold organically.
The Tao Te Ching doesn’t just speak of abstract ideals — it presents a model human being: the sage or Zhenren (the “true person”).
Qualities of the sage:
Detached from ego, fame, and competition.
Guided by inner clarity and humility.
Leads not by force, but by quiet example.
Taoism embraces this sage archetype, not as a saint, but as a fully natural human — integrated, grounded, and free from duality.
Laozi writes extensively about rulers and governance — using the Tao to guide statecraft.
“Governing a large country is like cooking a small fish. Too much handling will spoil it.”
This reflects a Taoist ethic of minimalism, decentralization, and moral restraint:
Don’t over-regulate.
Don’t impose rigid systems.
Lead by being, not by controlling.
This teaching profoundly shaped early Taoist political thought — as a counterpoint to Confucianism’s structured social order.
Although the Tao Te Ching is philosophical, it laid the groundwork for religious Taoism, which emerged centuries later.
Influences include:
The idea of Tao as the source of heaven and earth.
The reverence for balance (yin-yang) and emptiness (wu).
The concept of the immortal or perfected person (xian).
Religious Taoism integrated these with rituals, deities, and practices — but always kept the Tao at its metaphysical core.
The Tao Te Ching is rich in paradox:
“Soft overcomes hard.”
“The way forward is back.”
“To know that you do not know is the best.”
This nonlinear, poetic style teaches Taoists to:
See beyond dualistic thinking.
Embrace the unknowable.
Accept contradictions as part of truth.
Taoism thus evolves as a tradition that prizes intuition over logic and emptiness over certainty.
Because of the Tao Te Ching’s emphasis on:
Flow
Nature
Stillness
Uncarved simplicity (pu)
It influences not just theology, but aesthetics and daily living:
Taoist art emphasizes spontaneity and nature.
Taoist medicine values balance and internal energy.
Taoist diet, exercise (e.g., qigong), and rituals reflect effortless living.
The Tao Te Ching doesn’t just describe Taoism — it is Taoism.
Every major principle of Taoism can be traced back to its verses:
Tao as the Source
Wu Wei as practice
Simplicity as wisdom
Paradox as truth
Emptiness as fullness
Its timeless brevity and mystical tone allow it to remain relevant — not just as ancient scripture, but as a living guidebook for balance, freedom, and peace.
See lessWhat is the significance of meditation in Zen Buddhism?
1. Zazen: The Heart of Zen Practice In Zen Buddhism, zazen (seated meditation) is not merely a technique — it is the practice. The word “Zen” itself comes from the Sanskrit dhyāna, which means meditation. Zazen is not a means to an end. It is the end. Key Features of Zazen: Practiced with eyes open,Read more
In Zen Buddhism, zazen (seated meditation) is not merely a technique — it is the practice. The word “Zen” itself comes from the Sanskrit dhyāna, which means meditation.
Zazen is not a means to an end. It is the end.
Practiced with eyes open, facing a wall or natural space.
Focuses on posture, breath, and presence.
Letting thoughts arise and pass without attachment.
No mantra, visualization, or goal.
This style reflects the Zen ideal: radical simplicity, direct experience, and being fully present.
Zen does not teach enlightenment through study or belief. Instead, it emphasizes sudden insight (satori) — a flash of understanding or awakening — often cultivated during deep meditation.
Satori is not mystical escapism; it’s a direct perception of reality without filters.
Zazen creates the stillness and awareness necessary for such moments to occur.
As Zen Master Dōgen said:
“To study the Buddha Way is to study the self. To study the self is to forget the self.”
This forgetting of the self often happens in the stillness of zazen.
Zazen reveals the illusion of a fixed, separate self — the very source of suffering in Buddhist thought. Through quiet sitting:
The ego’s chatter quiets.
One witnesses impermanence and interconnectedness.
The mind stops grasping, labeling, and resisting.
This leads to non-dual awareness — a key theme in Zen — where distinctions between self and other dissolve.
In Zen, meditation isn’t confined to the cushion. It extends to every act — walking, eating, cleaning, speaking.
This reflects the idea of “everyday mind is the Way.”
When washing dishes, just wash dishes.
When walking, just walk.
This is meditation in action — a seamless life of mindfulness.
Thus, meditation trains the mind to be fully present in the ordinary, turning the mundane into the sacred.
Zen is known for its “direct transmission outside the scriptures.”
While traditional Buddhism reveres texts, Zen favors experiential wisdom.
Zazen becomes a silent teacher — one that leads to self-realization beyond words.
As a famous Zen saying goes:
“Don’t seek the truth. Just drop your opinions.”
Meditation is the act of dropping those opinions — layer by layer.
Meditation in Zen is also practiced in structured environments, like sesshin (intensive retreats) and daily zazen in Zen monasteries.
These sessions emphasize:
Routine and discipline
Group energy (sangha)
Ritual simplicity
Even in strict form, Zen meditation remains profoundly personal.
Zen meditation is not about achieving something. It’s about being with what is. It’s the practice of:
Observing reality directly,
Letting go of concepts,
Experiencing truth without filters.
It’s not about escaping life — but waking up to life in its raw, unfiltered form.
In Zen, meditation is the gate. But it is also the path, and ultimately, it becomes the destination itself.
See lessWhat valuable knowledge can I acquire in 10 minutes that will benefit me lifelong?
1. The 80/20 Principle (Pareto Principle) Lesson: 80% of results often come from 20% of efforts.Use it for life: Identify the small actions that lead to big outcomes. Focus on high-impact tasks in work, learning, and relationships.Learn in 10 minutes → Apply every day → Gain lifelong efficiency. 2.Read more
Lesson: 80% of results often come from 20% of efforts.
Use it for life:
Identify the small actions that lead to big outcomes.
Focus on high-impact tasks in work, learning, and relationships.
Learn in 10 minutes → Apply every day → Gain lifelong efficiency.
Lesson: Thoughts are mental events, not always truths.
Use it for life:
Helps manage overthinking and anxiety.
Supports mindfulness and emotional regulation.
A 10-minute mindset shift that rewires how you relate to stress and identity.
Lesson: If something takes less than 2 minutes, do it now.
Use it for life:
Keeps your to-do list short.
Builds momentum and avoids procrastination.
Small completions lead to big progress.
Lesson: Money grows exponentially when interest is earned on interest.
Use it for life:
Save early. Invest wisely. Let time do the heavy lifting.
Applicable to habits and learning too — small improvements compound.
Albert Einstein called it the “8th wonder of the world” for a reason.
Lesson: If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well.
Use it for life:
Learn the concept.
Explain it in simple language.
Identify gaps.
Refine and repeat.
Ten minutes of effort → Deeper understanding, faster retention.
Lesson: Saying no protects your time, energy, and goals.
Use it for life:
Practice saying: “Let me get back to you,” or “That doesn’t align with my priorities right now.”
Learn to say “no” → Say “yes” to what truly matters.
Lesson: Focus only on what you can control; let go of the rest.
Use it for life:
Lowers anxiety.
Sharpens decisions.
Reduces wasted energy.
A mental filter that promotes peace and power simultaneously.
Lesson:
Inhale 4 seconds → Hold 7 seconds → Exhale 8 seconds.
Use it for life:
Instantly lowers heart rate and anxiety.
Helps in stressful moments, interviews, and before sleep.
Ten minutes of practice → Lifelong emotional reset tool.
Lesson: Feedback reveals perception, not necessarily truth.
Use it for life:
Accept what helps, ignore what doesn’t.
Use it as a tool, not a label.
Reframe feedback, and you’ll fear it less and grow more.
Lesson: We overestimate how much others notice our flaws or actions.
Use it for life:
Frees you from self-consciousness.
Encourages bolder decisions and self-expression.
In 10 minutes, shed a lifetime of unnecessary anxiety.
In just 10 minutes, you can absorb a micro-idea that becomes a macro-upgrade in your thinking, living, and growing. These aren’t just “tips” — they are mental frameworks that serve as tools for decision-making, clarity, and resilience.
See lessWhich books are known to broaden one’s perspective?
Books That Broaden Perspectives: A Thoughtful Selection 1. “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari Why it broadens perspective: Offers a sweeping, interdisciplinary look at human history, combining anthropology, biology, and economics to question how societies and civilizationsRead more
Why it broadens perspective: Offers a sweeping, interdisciplinary look at human history, combining anthropology, biology, and economics to question how societies and civilizations evolved.
Unique insight: Challenges the reader to rethink human progress, culture, and the meaning of happiness.
Why it broadens perspective: Explores the dual systems of human thought — intuitive vs. analytical — shedding light on cognitive biases and decision-making.
Unique insight: Reveals how our minds work and why we often err, fostering self-awareness and critical thinking.
Why it broadens perspective: Combines Eastern philosophy and Western psychology to explore what true happiness means.
Unique insight: Encourages empathy, compassion, and mindfulness as tools for personal and collective growth.
Why it broadens perspective: Investigates the environmental and geographical reasons behind the unequal development of human societies.
Unique insight: Challenges simplistic explanations of history, emphasizing complex global interconnections.
Why it broadens perspective: A philosophical novel exploring absurdism and existentialism.
Unique insight: Invites readers to confront meaning, alienation, and individual freedom in a seemingly indifferent universe.
Why it broadens perspective: A memoir blending humor and tragedy, revealing the complexities of apartheid and post-apartheid South Africa.
Unique insight: Offers a deeply personal view of systemic racism, identity, and resilience.
Why it broadens perspective: Foundational feminist text analyzing the social construction of gender.
Unique insight: Provokes rethinking of gender roles, equality, and personal freedom.
Why it broadens perspective: Stoic philosophy from a Roman emperor’s personal reflections on life, duty, and virtue.
Unique insight: Promotes resilience, ethical living, and clarity of thought.
Why it broadens perspective: A historical novel narrated by Death, exploring humanity during WWII.
Unique insight: Highlights the power of words and the complexity of human morality amid conflict.
Why it broadens perspective: Addresses African American identity and invisibility in society.
Unique insight: Unpacks race, individuality, and social injustice in mid-20th-century America.
Cross-cultural understanding: They expose readers to diverse histories, philosophies, and social realities.
Critical thinking: They challenge ingrained biases and encourage questioning assumptions.
Emotional intelligence: They foster empathy through personal stories and ethical reflections.
Philosophical depth: They engage with existential questions about meaning, identity, and society.
Read actively: Take notes, reflect on themes, and connect ideas to current world events.
Discuss with others: Sharing perspectives enriches understanding.
Apply insights: Let the ideas inform your personal and professional life.
What are some innovative products or inventions that remain largely unknown?
10 Innovative Products and Inventions That Remain Largely Unknown 1. Air-Ink: Ink Made from Pollution What it is: Air-Ink is ink produced by capturing particulate matter from air pollution, transforming toxic carbon emissions into usable ink. Innovation: It turns a major environmental problem into aRead more
What it is: Air-Ink is ink produced by capturing particulate matter from air pollution, transforming toxic carbon emissions into usable ink.
Innovation: It turns a major environmental problem into a sustainable resource, offering a creative solution to air pollution.
Why lesser-known: It’s a niche eco-friendly product with limited commercial reach, mostly popular in art and environmental circles.
What it is: Portable devices that use solar energy to disinfect and purify water, using UV rays or heat.
Innovation: These purifiers are energy-efficient, require no chemicals, and can bring safe drinking water to remote areas.
Why lesser-known: Limited marketing and adoption in urban markets; primarily targeted at developing regions and emergency relief.
What it is: A device that mimics natural photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and CO₂ into energy-rich fuels like hydrogen or methanol.
Innovation: Offers a sustainable energy source that can potentially reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Why lesser-known: Still largely experimental and in research phases, with commercial applications years away.
What it is: A lamp that generates light by harnessing the energy from a descending weight, replacing the need for batteries or electricity.
Innovation: It’s low-cost, off-grid, and ideal for areas without reliable electricity.
Why lesser-known: Small-scale distribution focused on humanitarian projects limits broader market visibility.
What it is: Advanced metamaterials designed to bend light around objects, effectively rendering them invisible.
Innovation: Pushing the boundaries of optics and material science, with potential applications in defense and privacy.
Why lesser-known: High cost and technical complexity keep it in labs and defense sectors, away from public use.
What it is: Devices that use bacteria to convert organic matter into electricity.
Innovation: They can treat wastewater while simultaneously generating power—a win-win for energy and environment.
Why lesser-known: Early-stage technology with limited commercialization and awareness.
What it is: Concrete embedded with bacteria or special chemicals that activate to fill cracks autonomously.
Innovation: Extends the life of infrastructure, reducing repair costs and environmental impact.
Why lesser-known: Adoption is slow due to cost and lack of widespread awareness in construction industries.
What it is: Fabrics integrated with electronic components that can monitor health, adjust temperature, or provide connectivity.
Innovation: Merges fashion and technology for smart clothing that interacts with the wearer and environment.
Why lesser-known: High production cost and early development stage limit mass adoption.
What it is: A system of floating barriers designed to collect plastic waste from oceans autonomously.
Innovation: Addresses one of the most pressing environmental issues—ocean plastic pollution—using passive cleanup.
Why lesser-known: Operational complexity and funding challenges slow scaling; media coverage fluctuates.
What it is: Solar panels that can be integrated into windows and screens, generating electricity without blocking light.
Innovation: Enables buildings and devices to produce clean energy without altering aesthetics.
Why lesser-known: Still in prototype or early production phases with limited market penetration.
Niche applications: Some serve very specific markets or humanitarian purposes.
Early-stage development: Many are experimental or not yet commercialized.
High costs: Cutting-edge tech often has a premium price that limits adoption.
Limited marketing: Small startups or academic projects lack widespread promotion.
Regulatory hurdles: Especially in energy, health, or defense sectors.
Highlighting these innovations in mainstream media and tech blogs.
Supporting crowdfunding and pilot projects.
Encouraging partnerships with larger corporations or governments.
Fostering community engagement and educational campaigns.
“Which skills should I start learning now to stay ahead as a cloud developer in the future?” “भविष्य में एक क्लाउड डेवेलपर के रूप में आगे रहने के लिए मुझे अभी कौन-कौन सी स्किल्स सीखनी चाहिए?”
Skills to Learn Now to Stay Ahead as a Future-Ready Cloud Developer 1. Deep Cloud Platform Expertise Master at least one major cloud provider:Focus on platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Gain proficiency in core services: Compute (EC2, Azure VMs, Compute Engine) StorRead more
Master at least one major cloud provider:
Focus on platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Gain proficiency in core services:
Compute (EC2, Azure VMs, Compute Engine)
Storage (S3, Azure Blob, Cloud Storage)
Networking (VPC, Load Balancers)
Security (IAM, KMS)
Serverless (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions)
Learn multi-cloud strategies:
Understand how to architect and manage applications across multiple cloud platforms to avoid vendor lock-in and improve resilience.
Learn tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Azure ARM Templates, or Pulumi to automate cloud infrastructure deployment.
IaC enables repeatability, consistency, and scalability — a must-have for efficient cloud operations.
Master Docker for containerizing applications.
Dive deep into Kubernetes — the de facto standard for container orchestration.
Learn Helm Charts for Kubernetes application packaging.
Understand service meshes (e.g., Istio) and cloud-native patterns.
Learn to build automated CI/CD pipelines with tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps.
Understand continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment principles.
Familiarize yourself with monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and logging with ELK Stack.
Explore serverless computing to build highly scalable, cost-effective applications.
Get hands-on with AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions.
Understand event-driven architectures and microservices patterns.
Study cloud security fundamentals — identity and access management (IAM), encryption, secure networking, compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
Learn about Zero Trust Architecture and how to implement it in cloud environments.
Practice using security tools and services like AWS GuardDuty, Azure Security Center.
Understand how to design cloud-native apps optimized for scalability, availability, and resilience.
Learn about 12-factor app methodology, microservices, API gateways, and service discovery.
Cloud developers increasingly need skills in data pipelines, ETL, and analytics.
Learn cloud data services: AWS Glue, BigQuery, Azure Data Factory.
Explore how to integrate AI/ML services like AWS SageMaker, Azure ML, or Google AI Platform into your applications.
Be proficient in languages commonly used in cloud environments such as Python, Go, JavaScript/TypeScript, or Java.
Automate workflows using shell scripting or Python scripts.
Develop strong problem-solving and communication skills.
Understand business needs and translate them into technical solutions.
Stay adaptable, curious, and ready to learn new technologies quickly.
Edge Computing: Learn how cloud extends to the edge, including IoT integration.
GitOps: Automating infrastructure and deployments via Git repositories.
Cloud Cost Management: Optimizing cloud spend with tools and strategies.
Quantum Computing in Cloud: Early but growing area in providers like AWS Braket.
| Skill Area | Why It Matters | Recommended Tools/Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Platform Expertise | Foundation for all cloud development | AWS, Azure, GCP |
| Infrastructure as Code | Automation & scalability | Terraform, CloudFormation |
| Containers & Orchestration | Efficient app deployment & management | Docker, Kubernetes, Helm |
| DevOps & CI/CD | Speed & reliability in software delivery | Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI |
| Serverless Architectures | Cost-effective & scalable apps | AWS Lambda, Azure Functions |
| Cloud Security | Protect data & apps | IAM, KMS, GuardDuty, Zero Trust |
| Cloud-Native Development | Build resilient & scalable apps | Microservices, API Gateways |
| Data & AI/ML Integration | Enhance apps with data insights & AI | AWS SageMaker, BigQuery, Azure ML |
| Programming & Scripting | Core development & automation | Python, Go, JavaScript |
| Soft Skills & Business Acumen | Align tech solutions with business needs | Communication, problem-solving |
The cloud landscape evolves rapidly, so continuous learning is vital. Building a strong foundation now with these skills will position you as a versatile, future-proof cloud developer ready to innovate and lead.
See less
Introduction: The Eternal Hymn of Detachment and Devotion Shiv Rudrashtakam is one of the most profound Sanskrit hymns dedicated to Lord Shiva, the supreme yogi, destroyer of ignorance, and embodiment of pure consciousness. Composed by Adi Shankaracharya, this eight-verse stotra ...

A Prime-Adam Number is defined as a positive number that fulfills two conditions simultaneously: it is a prime number and also an Adam number. For example, take the number 13; its reverse is 31. The square of 13 is 169, and the ...

Introduction The 74th Miss Universe pageant, held on November 21, 2025, at the Impact Challenger Hall in Nonthaburi, Thailand, set a new benchmark in global beauty contests. Not merely a showcase of beauty and fashion, this year’s event stood as ...

A Keith number is an n-digit number that appears as a term in a sequence, where the first n terms are its own digits, and each following term is the sum of the previous n terms. For example, 197 is ...

A matrix is called Doubly Markov if it satisfies the following conditions: All elements are greater than or equal to 0. The sum of each row is equal to 1. The sum of each column is equal to 1. The program should ...

The Dawn of a Clean Energy Revolution Imagine a world where air pollution is history, industries run clean, and the very fuel that powers our lives leaves nothing behind but water vapor. Sounds like science fiction? It’s the promise of ...
The "mixture of experts" (MoE) technique significantly enhances DeepSeek-R1's efficiency through several innovative mechanisms that optimize resource utilization and improve performance. Here’s how this architecture contributes to the model's overall effectiveness: Selective Activation of Experts: DRead more
The “mixture of experts” (MoE) technique significantly enhances DeepSeek-R1’s efficiency through several innovative mechanisms that optimize resource utilization and improve performance. Here’s how this architecture contributes to the model’s overall effectiveness:
Conclusion
The “mixture of experts” technique is central to DeepSeek-R1’s design, allowing it to achieve remarkable efficiency and performance in handling complex AI tasks. By leveraging selective activation, specialization, intelligent routing through gating networks, and effective load balancing, DeepSeek-R1 not only reduces computational costs but also enhances its ability to deliver precise and contextually relevant outputs across various domains. This innovative architecture positions DeepSeek-R1 as a competitive player in the AI landscape, challenging established models with its advanced capabilities.
See less