If cars are available in petrol and diesel variants then why is this option not available in the bikes ?
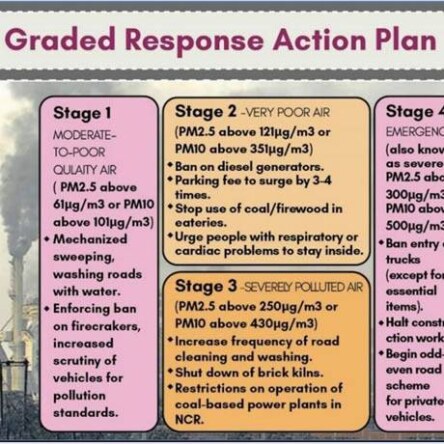
GRAP Stage 3 entails a ban on non-essential construction work. Classes up to grade V are required to shift to hybrid mode under Stage 3. Parents and students have the option to choose online education wherever available. Under Stage 3, the use of BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel cars (4-wheelers) is rRead more
GRAP Stage 3 entails a ban on non-essential construction work. Classes up to grade V are required to shift to hybrid mode under Stage 3. Parents and students have the option to choose online education wherever available.
Under Stage 3, the use of BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel cars (4-wheelers) is restricted in Delhi and nearby NCR districts. Persons with disabilities are exempt.
Stage 3 also bans non-essential diesel-operated medium goods vehicles with BS-IV or older standards in Delhi. The Stage 3 of GRAP was lifted on December 27 after a marked improvement in Delhi’s air quality following day-long rainfall in the national capital.
Throughout 2024, Delhi recorded the highest number of ‘severe’ AQI days since 2022, with 17 days exceeding an AQI of 400. Additionally, 70 days were classified as ‘very poor’. Not a single ‘good’ air quality day was recorded in 2024, a first since 2018.
See less






Motorcycles are predominantly available in petrol variants, with very few diesel options. This is due to several technical and practical reasons: Engine Size and Weight Diesel engines are typically heavier and larger than petrol engines of equivalent power output. For motorcycles, where weight and sRead more
Motorcycles are predominantly available in petrol variants, with very few diesel options. This is due to several technical and practical reasons:
While there have been a few diesel motorcycle models developed for specific purposes (like military use), these are exceptions rather than the norm due to the above challenges.
See less