Which of the following fields is AlphaFold2 related?
Poll Results
Please login to vote and see the results.
Sign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
At Qukut, our mission is to bridge the gap between knowledge seekers and knowledge sharers. We strive to unite diverse perspectives, fostering understanding and empowering everyone to contribute their expertise. Join us in building a community where knowledge flows freely and growth is limitless.
Which of the following fields is AlphaFold2 related?
Please login to vote and see the results.
What is ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder)?
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can interfere with daily functioning and development. Symptoms of ADHD often includeRead more
ADHD (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can interfere with daily functioning and development. Symptoms of ADHD often include difficulty focusing, forgetfulness, trouble following through on tasks, restlessness, and impulsive behavior. There are three main types of ADHD:
ADHD is often managed through a combination of behavioral therapy, lifestyle changes, and medication, depending on the severity and individual needs.
See lessWhat is cold-start data?
Cold-start data refers to data used to train or adapt a machine learning model in scenarios where there is little to no prior information available about a new task, user, domain, or context. The term originates from the "cold-start problem"—a common challenge in systems like recommendation engines,Read more
Cold-start data refers to data used to train or adapt a machine learning model in scenarios where there is little to no prior information available about a new task, user, domain, or context. The term originates from the “cold-start problem”—a common challenge in systems like recommendation engines, where a model struggles to make accurate predictions for new users, items, or environments due to insufficient historical data. In the context of AI training (e.g., DeepSeek-R1), cold-start data is strategically incorporated to address similar challenges and improve the model’s adaptability and robustness.
Cold-start data is critical for building AI systems that remain effective in dynamic, unpredictable environments. By training models to handle “unknowns,” it ensures they stay relevant, fair, and robust—even when faced with novel challenges.
See lessHow does the scoring system work in synchronized swimming?
Discuss the role of peer pressure on an adolescent’s personality development
A rainbow is caused by sunlight and atmospheric conditions. Light enters a water droplet, slowing down and bending as it goes from air to denser water. The light reflects off the inside of the droplet, separating into its component wavelengths--or colors.
A rainbow is caused by sunlight and atmospheric conditions. Light enters a water droplet, slowing down and bending as it goes from air to denser water. The light reflects off the inside of the droplet, separating into its component wavelengths–or colors.
See lessHow to become healthy?
Becoming healthy involves a holistic approach that encompasses physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Here are actionable steps to help you achieve and maintain a healthy lifestyle: 1. Focus on a Balanced Diet Eat Whole Foods: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, aRead more
Becoming healthy involves a holistic approach that encompasses physical, mental, and emotional well-being. Here are actionable steps to help you achieve and maintain a healthy lifestyle:
Becoming healthy requires a balanced approach that addresses diet, exercise, mental well-being, and regular medical care. Embrace a lifestyle that fosters overall wellness, and be consistent in your efforts to make health a priority.
See lessThe pH scale is a numerical scale used to measure the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating alkalinity. Key Points of the pH Scale Definition: pH stands for "potential of hydrogenRead more
The pH scale is a numerical scale used to measure the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, values below 7 indicating acidity, and values above 7 indicating alkalinity.
The pH scale helps to understand the chemical nature of substances and their interactions in various environments and biological systems.
See lessWhat is a money bill??
A Money Bill is a specific type of bill in a legislative system that deals exclusively with national revenue or expenditure. In the context of India, a Money Bill is defined under Article 110 of the Indian Constitution and can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha, not the Rajya Sabha. Features of a MRead more
A Money Bill is a specific type of bill in a legislative system that deals exclusively with national revenue or expenditure. In the context of India, a Money Bill is defined under Article 110 of the Indian Constitution and can only be introduced in the Lok Sabha, not the Rajya Sabha.
Understanding these features helps differentiate a Money Bill from other types of bills in the legislative process.
See lessWhat are the key ideas of existential nihilism?
Existential nihilism is a philosophical perspective that explores the nature of existence, often emphasizing the absence of intrinsic meaning or purpose in life. Below are its key ideas: 1. Absence of Intrinsic Meaning Existential nihilism posits that life has no inherent meaning, value, or purpose.Read more
Existential nihilism is a philosophical perspective that explores the nature of existence, often emphasizing the absence of intrinsic meaning or purpose in life. Below are its key ideas:
In essence, existential nihilism is not purely pessimistic; it is a lens through which one can view the world and a starting point for existential exploration, ultimately leaving individuals with the challenge—and freedom—of creating their own meaning.
See lessThe haka is a traditional Māori ceremonial dance or challenge originating from the indigenous people of New Zealand. It is characterized by vigorous movements, rhythmic chanting, and often fierce facial expressions, such as protruding tongues and bulging eyes. Traditionally performed by warriors befRead more
The haka is a traditional Māori ceremonial dance or challenge originating from the indigenous people of New Zealand. It is characterized by vigorous movements, rhythmic chanting, and often fierce facial expressions, such as protruding tongues and bulging eyes. Traditionally performed by warriors before battle, the haka was intended to intimidate opponents while also expressing the strength, unity, and determination of the performers.
There are various types of haka, each with its specific purpose and meaning:
One of the most famous haka is “Ka Mate,” composed in the early 19th century by the Māori chief Te Rauparaha. It celebrates survival and is commonly performed by the All Blacks. Its words convey the triumph of life over death.
Haka is more than a dance; it’s a profound expression of emotion, culture, and identity.
See lessWhat is the process of fermentation?
Fermentation is a biological process in which microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, or molds, break down organic compounds—typically sugars—into simpler compounds like alcohol or acids, in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic conditions). It is an energy-producing process that allows cells to generatRead more
Fermentation is a biological process in which microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, or molds, break down organic compounds—typically sugars—into simpler compounds like alcohol or acids, in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic conditions). It is an energy-producing process that allows cells to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for energy when oxygen is not available for aerobic respiration. The specific outcome of fermentation depends on the type of organism and the substrate involved.
While fermentation does not generate as much energy (ATP) as aerobic respiration, it allows organisms to survive and produce energy in oxygen-deprived environments.
Fermentation is an anaerobic metabolic process where cells convert glucose into simpler molecules like alcohol or lactic acid, producing ATP without the need for oxygen. It plays a crucial role in energy production under low-oxygen conditions and has wide applications in food production and biotechnology.
See lessWhich one of the following makes a tool with a stick to scrape insects from a hole in a tree or a log of wood? ...Read more
Please login to vote and see the results.
Orangutans are known for their intelligence and ability to use tools. They have been observed using sticks to extract insects from holes in trees or logs, demonstrating advanced problem-solving skills and tool use in their natural environment. The correct answer is Orangutan.
Orangutans are known for their intelligence and ability to use tools. They have been observed using sticks to extract insects from holes in trees or logs, demonstrating advanced problem-solving skills and tool use in their natural environment. The correct answer is Orangutan.
See lessWhat is the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy?
Aspect Renewable Energy Non-Renewable Energy Definition Energy from replenishable natural resources (e.g., sunlight, wind). Energy from finite resources that take millions of years to form (e.g., coal, oil). Availability Virtually inexhaustible; naturally replenished. Limited; depletes over time andRead more
| Aspect | Renewable Energy | Non-Renewable Energy |
| Definition | Energy from replenishable natural resources (e.g., sunlight, wind). | Energy from finite resources that take millions of years to form (e.g., coal, oil). |
| Availability | Virtually inexhaustible; naturally replenished. | Limited; depletes over time and cannot be replenished quickly. |
| Examples | Solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, biomass. | Coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear (uranium, plutonium). |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal; low greenhouse gas emissions; eco-friendly. | High; significant greenhouse gas emissions and pollution. |
| Cost and Infrastructure | High initial investment but low operational costs; requires storage solutions. | Established infrastructure, cheaper initially but costly long-term due to environmental damage. |
| Sustainability | Sustainable for long-term use if managed responsibly. | Unsustainable due to finite reserves and environmental consequences. |
| Global Impact | Promotes energy security, widely available resources. | Dependence on finite resources can lead to energy crises. |
See less
What is the next number in the series: 10, 9, 11, 8, 12, 7, ___
Answer will be 13 as 7+6=13
Answer will be 13 as 7+6=13
See lessHow does altitude affect endurance in long-distance running?
Altitude significantly affects endurance in long-distance running due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Here's a detailed breakdown of how altitude impacts performance: Reduced Oxygen Availability At higher altitudes, the atmospheric pressure is lower, which leads to a decrease in the partial pRead more
Altitude significantly affects endurance in long-distance running due to the reduced availability of oxygen. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how altitude impacts performance:
Altitude poses a challenge to endurance in long-distance running by limiting oxygen availability, but with proper acclimatization, athletes can adapt and potentially gain a competitive edge when returning to lower altitudes.
See lesswhat is the difference between branches of psychology and application of psychology?
Psychology is derived from the word "psyche" which means mind and "logy" which means study of something hence, psychology means the scientific study of human mind and behaviour. While application of psychology includes many fields like sports schools and colleges clinical therauptic environment workRead more
Psychology is derived from the word “psyche” which means mind and “logy” which means study of something hence, psychology means the scientific study of human mind and behaviour.
While application of psychology includes many fields like
sports
schools and colleges
clinical
therauptic
environment
workplace especially industries
social setups
forensic
health
community
developmental
personality building
Psychology is an emerging field which has its application not only limited to the above mentioned fields but is trying to reach and fit in through as many fields as possible.
Hence, psychology is an umbrella term which covers in itself the study of human behaviour and its fields are the areas where psychology can be applied and could be taken as a part to improve the performance of the subjects.
What is a renewable energy source?
A renewable energy source is a natural resource that can be replenished or regenerated naturally over a short period of time and is considered sustainable for long-term use. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are not depleted when used and have minimal environmental impact. Examples of ReRead more
A renewable energy source is a natural resource that can be replenished or regenerated naturally over a short period of time and is considered sustainable for long-term use. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are not depleted when used and have minimal environmental impact.
Renewable energy is crucial for a sustainable future as it helps preserve natural resources and reduces environmental degradation.
See lessWhat were the reasons for the Great Revolt of 1857 in India???
Causes Behind the Great Revolt of 1857 The Great Revolt of 1857 was a watershed moment in Indian history, caused by a combination of political, economic, social, cultural, and military factors. However, it is debated whether it can truly be called the "First War of Independence" since the movement lRead more
The Great Revolt of 1857 was a watershed moment in Indian history, caused by a combination of political, economic, social, cultural, and military factors. However, it is debated whether it can truly be called the “First War of Independence” since the movement lacked nationalistic unity, and most leaders fought for local or personal reasons rather than a unified national cause. Below is a detailed account of the causes, with a discussion on why it was not a nationalist movement.
Each of these leaders had localized ambitions, and there was no concerted effort or vision to overthrow British rule across the subcontinent.
Conclusion
While the Great Revolt of 1857 was a significant challenge to British authority, it lacked the ideological and organizational unity required to be termed a “war of independence.” The rebellion reflected widespread grievances against British policies, but the absence of a cohesive nationalist agenda and the localized ambitions of its leaders underscore why it cannot be seen as India’s first unified fight for freedom. Nonetheless, it laid the foundation for future struggles, which eventually culminated in the Indian independence movement led by a united nationalist front.
See lessWhat are the benefits and risks of intermittent fasting?
Please login to vote and see the results.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting Intermittent fasting has been shown to provide several potential health benefits: Weight loss and fat burning: Fasting puts your body into a fat-burning state and may slightly boost metabolism, leading to weight loss. Reduced insulin resistance and blood sugar levelsRead more
Intermittent fasting has been shown to provide several potential health benefits:
In summary, while intermittent fasting shows promise for weight loss and improved health markers, more research is needed on its long-term sustainability and effects. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new diet, especially if you have a medical condition or are in a high-risk group.
See lessHow does sustainable architecture impact urban planning?
Sustainable architecture significantly impacts urban planning in several ways: Energy Efficiency: Sustainable architecture promotes the use of energy-efficient buildings, which requires urban planners to prioritize renewable energy sources, green buildings, and the development of energy-conscious ciRead more
Sustainable architecture significantly impacts urban planning in several ways:
By incorporating sustainable architecture principles, urban planning shifts toward creating cities that are environmentally friendly, resource-efficient, and focused on long-term livability.
See lessWhat is the role of the nervous system in the body?
The nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating and regulating various functions of the body. It is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body, allowing for communication, control, and integration of bodily functions. The nervous system consists of the brain, spRead more
The nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating and regulating various functions of the body. It is responsible for transmitting signals between different parts of the body, allowing for communication, control, and integration of bodily functions. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves that spread throughout the body.
The nervous system is essential for nearly all aspects of life, from basic functions like breathing and heart rate regulation to complex cognitive processes like memory, learning, and emotion. It enables the body to react to changes in the environment and maintain a stable internal state, ensuring overall health and survival.
See lessWhat is Dunning-Kruger Effect?
The Dunning-Kruger Effect is a cognitive bias in which people with low ability or knowledge in a specific area overestimate their own competence. Essentially, individuals who are less skilled or knowledgeable in a subject tend to have an inflated sense of their ability, while those who are more expeRead more
The Dunning-Kruger Effect is a cognitive bias in which people with low ability or knowledge in a specific area overestimate their own competence. Essentially, individuals who are less skilled or knowledgeable in a subject tend to have an inflated sense of their ability, while those who are more experienced or knowledgeable may underestimate their own expertise.
This effect occurs because people with limited knowledge or skills in a domain often lack the awareness to recognize their shortcomings. The Dunning-Kruger Effect was identified in 1999 by psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger, who conducted a series of experiments that demonstrated this phenomenon.
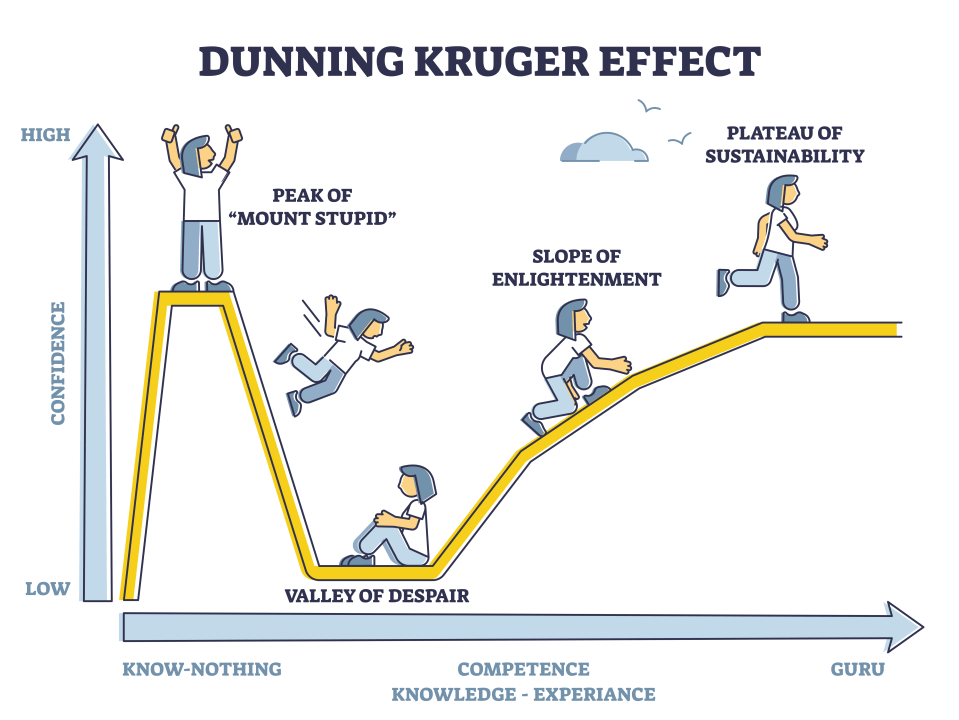
Source: LinkedIn
Key aspects of the Dunning-Kruger Effect include:
In summary, the Dunning-Kruger Effect highlights the paradox that those with the least knowledge in a domain are often the most confident about their skills in it.
See lessTell me everything about qukut?
What is Qukut? Qukut is a social question-and-answer platform designed to empower users by combining knowledge sharing with the ability to earn money. It serves as a space where users can: Ask questions: Gain insights and answers to diverse queries. Answer questions: Share expertise and earn rewardsRead more
Qukut is a social question-and-answer platform designed to empower users by combining knowledge sharing with the ability to earn money. It serves as a space where users can:
Qukut bridges the gap between social networking, learning, and earning:
Why did the Roman Empire fall?
The lack of loyalty from the military and the distrust in the government among Romans were perhaps the biggest reasons for the fall of the Roman Empire.
The lack of loyalty from the military and the distrust in the government among Romans were perhaps the biggest reasons for the fall of the Roman Empire.
See lessThe "large-scale structure" (LSS) of the universe refers to the distribution of galaxies, clusters, superclusters, and voids across the cosmos. These structures provide critical insights into the nature of dark matter (DM), as it is thought to play a fundamental role in the formation and evolution oRead more
The “large-scale structure” (LSS) of the universe refers to the distribution of galaxies, clusters, superclusters, and voids across the cosmos. These structures provide critical insights into the nature of dark matter (DM), as it is thought to play a fundamental role in the formation and evolution of these structures. The presence of dark matter (including various models like cold dark matter (CDM) and self-interacting dark matter (SIDM)) has significant implications for LSS, and discrepancies between the predictions of cosmological simulations and actual observations have raised important questions about the properties of dark matter. Below, I explore how the LSS challenges our understanding of dark matter properties, particularly in the context of SIDM, and how future surveys like the EUCLID mission can help resolve these tensions.
The EUCLID mission, set to launch in the near future, will be one of the most important tools for resolving tensions between cosmological simulations and observations of large-scale structure. Here’s how it will help:
The large-scale structure of the universe presents a critical challenge to our understanding of dark matter, particularly in terms of the formation of superclusters and voids. The tension between predictions from cold dark matter (CDM) simulations and actual observations of galactic clustering and the distribution of voids has led to the exploration of alternative models, such as self-interacting dark matter (SIDM).
Future surveys, particularly the EUCLID mission, will play a pivotal role in resolving these tensions. By providing detailed measurements of the distribution of galaxies, voids, and galaxy clusters, along with weak lensing data, EUCLID will offer new insights into the nature of dark matter, testing the predictions of both SIDM and CDM models. Ultimately, these findings will help to refine our understanding of the cosmological parameters that govern the growth of structures in the universe and lead to a better grasp of dark matter’s role in shaping the cosmos.
See lessWhat is the speed of light?
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
See lessHow does the “chain-of-thought” reasoning improve the accuracy of DeepSeek-R1 ?
How does organic farming impact soil health?
create humus-rich top-soils, restore diversity above and below ground, retain water and contribute to solutions to water pollution. On average, organic farms host 34% more biodiversity than conventional ones.
create humus-rich top-soils, restore diversity above and below ground, retain water and contribute to solutions to water pollution. On average, organic farms host 34% more biodiversity than conventional ones.
See lessWhat is the difference between speed and velocity?
speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity so that is different.
speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity so that is different.
See lessWhat are the key strategies in professional curling?

Introduction: The Eternal Hymn of Detachment and Devotion Shiv Rudrashtakam is one of the most profound Sanskrit hymns dedicated to Lord Shiva, the supreme yogi, destroyer of ignorance, and embodiment of pure consciousness. Composed by Adi Shankaracharya, this eight-verse stotra ...

A Prime-Adam Number is defined as a positive number that fulfills two conditions simultaneously: it is a prime number and also an Adam number. For example, take the number 13; its reverse is 31. The square of 13 is 169, and the ...

Introduction The 74th Miss Universe pageant, held on November 21, 2025, at the Impact Challenger Hall in Nonthaburi, Thailand, set a new benchmark in global beauty contests. Not merely a showcase of beauty and fashion, this year’s event stood as ...

A Keith number is an n-digit number that appears as a term in a sequence, where the first n terms are its own digits, and each following term is the sum of the previous n terms. For example, 197 is ...

A matrix is called Doubly Markov if it satisfies the following conditions: All elements are greater than or equal to 0. The sum of each row is equal to 1. The sum of each column is equal to 1. The program should ...

The Dawn of a Clean Energy Revolution Imagine a world where air pollution is history, industries run clean, and the very fuel that powers our lives leaves nothing behind but water vapor. Sounds like science fiction? It’s the promise of ...
AlphaFold2, an AI system developed by DeepMind, has significantly impacted the field of protein structure prediction. It can predict the 3D structure of nearly every known protein, a scientific achievement that helps in understanding biological processes. The tool has revolutionized biology, as evidRead more
AlphaFold2, an AI system developed by DeepMind, has significantly impacted the field of protein structure prediction. It can predict the 3D structure of nearly every known protein, a scientific achievement that helps in understanding biological processes. The tool has revolutionized biology, as evidenced by its recognition through awards like the Nobel Prize.
Therefore, answer is Protein Structure Prediction
See less