What is the function of the digestive system?
Fossils are the preserved remains, impressions, or traces of organisms that lived in the past. These can include bones, shells, leaves, or even footprints. Fossils provide important insights into the history of life on Earth, showing how different species have evolved over millions of years. How FosRead more
Fossils are the preserved remains, impressions, or traces of organisms that lived in the past. These can include bones, shells, leaves, or even footprints. Fossils provide important insights into the history of life on Earth, showing how different species have evolved over millions of years.
How Fossils Are Formed
Fossil formation, or fossilization, is a rare occurrence that usually involves several key steps:
- Death of the Organism: The process begins when an organism dies. To become a fossil, the organism must be buried quickly to protect it from scavengers and decay.
- Burial: The dead organism is covered by sediment such as mud, sand, or volcanic ash. Rapid burial helps preserve the remains by cutting off exposure to air and bacteria that promote decay.
- Sedimentation: Over time, layers of sediment build up over the organism. These layers gradually compress and harden into sedimentary rock, encasing the remains.
- Mineralization: As water percolates through the sediment, minerals dissolved in the water replace the organic material in the remains, turning them into stone. This process is called permineralization.
- Exposure: Geological processes such as erosion or tectonic activity eventually bring the fossil back to the Earth’s surface, where it can be discovered.
Types of Fossils
- Body Fossils: Direct remains of the organism, such as bones, teeth, or shells.
- Trace Fossils: Indirect evidence of an organism’s presence, such as footprints, burrows, or feces.
- Molds and Casts: Impressions left in the sediment where an organism was buried. A mold is a hollow impression, while a cast is formed when that mold is filled with minerals.
Fossils are crucial for understanding the Earth’s history, the evolution of life, and the environments of the past.
See less
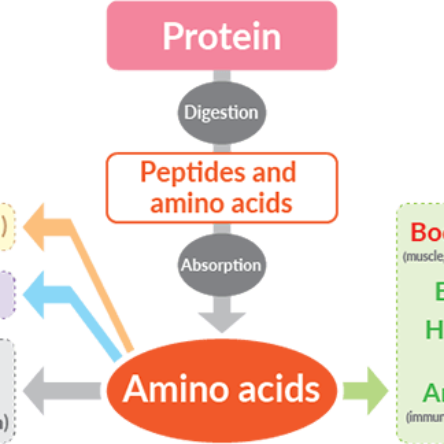






The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, which the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and cell repair. It also plays a crucial role in eliminating waste. Here's a breakdown of its main functions: Functions of the Digestive System Ingestion: The process begiRead more
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, which the body can absorb and use for energy, growth, and cell repair. It also plays a crucial role in eliminating waste. Here’s a breakdown of its main functions:
Functions of the Digestive System
Each part of the digestive system, from the mouth to the anus, plays a specific role in ensuring that the body gets the nutrients it needs and effectively eliminates waste.
See less