Introduction
In a significant medical advancement, Russia has announced the development of an mRNA cancer vaccine, with plans to distribute it to patients free of charge starting in early 2025. This initiative, led by the Russian Ministry of Health in collaboration with several research centers, represents a promising advancement in cancer treatment.
mRNA vaccines have gained prominence due to their role in combating infectious diseases like COVID-19. Their application in oncology is now being explored, offering a novel approach to cancer immunotherapy. Unlike traditional vaccines, mRNA vaccines work by instructing cells to produce specific proteins that trigger an immune response, enabling the body to recognize and attack cancer cells.
The significance of Russia’s development extends beyond its national borders. Cancer remains a leading cause of death worldwide, and the introduction of an effective mRNA-based vaccine could revolutionize global cancer treatment protocols. By providing this vaccine free of charge, Russia aims to enhance accessibility to cutting-edge therapies, potentially improving survival rates and quality of life for cancer patients.
This development also underscores the growing importance of mRNA technology in medical research. The success of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated interest in their potential applications for other diseases, including cancer. Researchers are optimistic that mRNA vaccines can be tailored to target various types of cancer, offering personalized treatment options with fewer side effects compared to conventional therapies.
Russia’s announcement of a free mRNA-based cancer vaccine marks a pivotal moment in the global fight against cancer. As the medical community continues to explore and develop mRNA technology, such innovations hold the promise of transforming cancer care and bringing us closer to more effective and accessible treatments worldwide.
Understanding mRNA Cancer Vaccines
Messenger RNA (mRNA) cancer vaccines represent a cutting-edge approach in oncology, leveraging the body’s own cellular machinery to combat cancer.
Explanation of mRNA Vaccine Technology and Its Role in Cancer Treatment
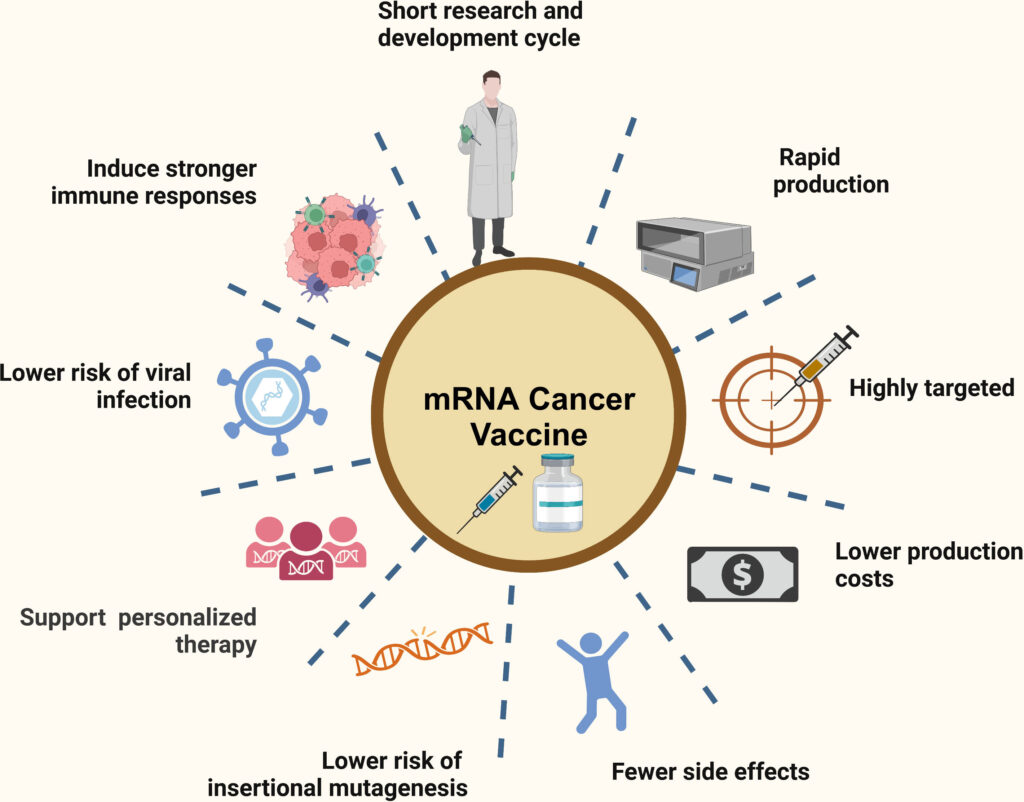
mRNA vaccines function by introducing synthetic mRNA sequences into the body, which encode specific tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) or neoantigens unique to cancer cells. Once inside the body’s cells, this mRNA is translated into proteins that mimic these antigens. The immune system recognizes these proteins as foreign, prompting an immune response that targets and destroys cancer cells expressing the same antigens.
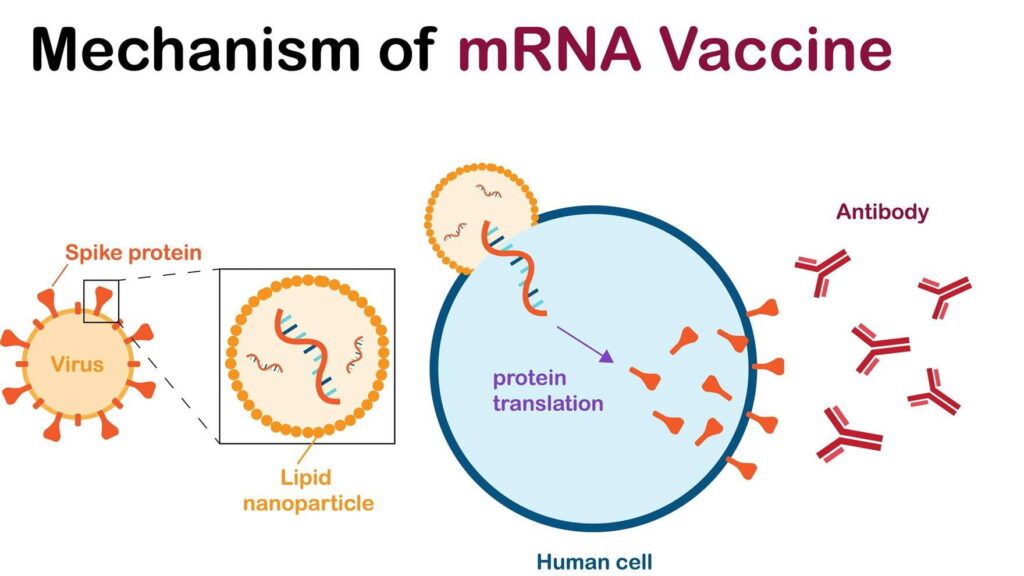
This method offers several advantages:
- Precision: By targeting specific antigens present on cancer cells, mRNA vaccines can minimize damage to healthy tissues.
- Adaptability: mRNA sequences can be rapidly designed and synthesized, allowing for the development of personalized vaccines tailored to an individual’s unique tumor profile.
- Safety: As mRNA does not integrate into the genome, there is no risk of genetic alterations in the patient’s DNA.
Comparison with Traditional Cancer Treatments and Vaccines
Traditional cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, are often non-specific, targeting rapidly dividing cells indiscriminately. While effective in reducing tumor size, these treatments can also harm healthy cells, leading to significant side effects like fatigue, nausea, and increased susceptibility to infections.
In contrast, mRNA cancer vaccines aim to elicit a targeted immune response against cancer cells, potentially reducing collateral damage to normal tissues. This specificity may result in fewer side effects and improved patient quality of life.
Conventional vaccines, such as those for infectious diseases, typically introduce inactivated pathogens or their components to stimulate immunity. However, cancer vaccines face the challenge of distinguishing between normal and malignant cells, as cancer arises from the body’s own tissues. mRNA vaccines address this by encoding antigens that are either uniquely expressed or overexpressed in cancer cells, enhancing the immune system’s ability to differentiate and target malignancies.
Furthermore, the production of traditional vaccines can be time-consuming and complex, involving the cultivation of pathogens or proteins. mRNA vaccines streamline this process, as they can be synthesized chemically, allowing for rapid development and scalability.
mRNA cancer vaccines offer a novel and promising avenue for cancer treatment, combining specificity, adaptability, and safety. Their development marks a significant advancement over traditional therapies, with the potential to transform oncology by providing more effective and personalized treatment options.
Details of Russia’s mRNA Cancer Vaccine
Russia has recently announced the development of an mRNA-based cancer vaccine, marking a significant advancement in oncology.
Development Process and Key Institutions Involved
The vaccine’s development is a collaborative effort spearheaded by the Gamaleya National Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology, renowned for its role in creating the Sputnik V COVID-19 vaccine. Working alongside the Russian Ministry of Health’s Research Center for Radiology, these institutions have combined their expertise in immunology and molecular biology to develop a vaccine aimed at enhancing the body’s immune response against cancer cells.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence in Accelerating Vaccine Development
A notable aspect of this initiative is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into the vaccine development process. AI algorithms have been employed to analyze vast datasets, identifying optimal tumor-associated antigens to target. This computational approach significantly reduces the time required for vaccine design, enabling the creation of personalized mRNA vaccines tailored to individual patients’ tumor profiles. By leveraging AI, researchers can expedite the development process, potentially generating personalized vaccine formulations within a remarkably short timeframe.
Pre-Clinical Trial Results Demonstrating Effectiveness in Tumor Suppression and Metastasis Reduction
Pre-clinical trials of the mRNA cancer vaccine have yielded promising results. Studies indicate that the vaccine effectively suppresses tumor growth and reduces the risk of metastasis, the spread of cancer to other parts of the body. These findings suggest that the vaccine not only targets existing cancer cells but may also impede the progression of the disease, offering a dual benefit in cancer therapy. The success of these pre-clinical trials has paved the way for subsequent clinical trials to further assess the vaccine’s safety and efficacy in human subjects.
Russia’s development of an mRNA-based cancer vaccine, facilitated by leading research institutions and accelerated through AI integration, represents a significant stride in cancer treatment. The encouraging pre-clinical results underscore the potential of this innovative approach to improve patient outcomes by effectively suppressing tumors and reducing metastasis.
Implementation and Accessibility
Russia is poised to make a significant impact on cancer treatment accessibility with its recent announcement of an mRNA-based cancer vaccine.
Plans for Free Distribution to Patients Starting in Early 2025
The Russian Ministry of Health has declared that this innovative vaccine will be available to patients at no cost, with distribution set to commence in early 2025. This initiative underscores the government’s commitment to public health and its dedication to providing cutting-edge medical treatments to its citizens.
Potential Impact on Public Health and Cancer Treatment Accessibility in Russia
The introduction of a free mRNA-based cancer vaccine is anticipated to have profound effects on public health in Russia:
- Enhanced Accessibility: By eliminating financial barriers, the vaccine becomes accessible to a broader segment of the population, including those in economically disadvantaged regions.
- Early Intervention: Widespread availability may encourage early vaccination, potentially leading to the prevention of cancer development or the reduction of tumor progression in at-risk individuals.
- Healthcare System Relief: A decrease in cancer incidence and progression could alleviate the burden on healthcare facilities, allowing resources to be allocated more efficiently.
- Public Trust and Compliance: Government-funded health initiatives can bolster public trust in medical advancements, leading to higher acceptance and compliance rates.
Russia’s plan to distribute the mRNA-based cancer vaccine free of charge is a landmark move that could transform cancer care within the country. By enhancing accessibility and promoting early intervention, this initiative has the potential to improve survival rates and quality of life for countless individuals, setting a precedent for public health strategies worldwide.
Global Implications
The global landscape of cancer treatment is undergoing a transformative shift with the advent of mRNA-based vaccines. Russia’s recent announcement of its own mRNA cancer vaccine adds a significant chapter to this evolving narrative.
Comparison with Cancer Vaccine Developments in Other Countries
Several nations are actively exploring mRNA technology for cancer therapeutics:
- United States: Biotechnology firms, notably Moderna and BioNTech, have initiated clinical trials for personalized mRNA cancer vaccines targeting melanoma and other malignancies. These vaccines are designed to elicit immune responses against tumor-specific antigens, aiming to prevent cancer recurrence.
- United Kingdom: The National Health Service (NHS) has embarked on trials to provide bespoke cancer treatments to patients, potentially benefiting thousands. This initiative underscores the UK’s commitment to integrating advanced mRNA vaccine technology into standard cancer care.
- Germany: BioNTech, a pioneer in mRNA technology, is conducting trials for various cancer types, leveraging insights gained from COVID-19 vaccine development to expedite cancer vaccine research.
Russia’s entry into the mRNA cancer vaccine arena positions it among these leading nations, contributing to a global effort to revolutionize cancer treatment.
Potential Influence on Global Cancer Treatment Protocols and Research Initiatives
The development of mRNA cancer vaccines holds several implications for global oncology practices:
- Standardization of mRNA Vaccines: As more countries develop and approve mRNA-based cancer vaccines, these treatments may become integral to international cancer care protocols, offering standardized, effective options for patients worldwide.
- Acceleration of Research: Russia’s advancements may stimulate increased investment and collaboration in cancer vaccine research globally, fostering a competitive environment that accelerates innovation and clinical application.
- Accessibility and Equity: Russia’s commitment to free distribution sets a precedent that could influence global health policies, emphasizing the importance of making advanced cancer treatments accessible to diverse populations, thereby addressing disparities in healthcare access.
Russia’s development of an mRNA-based cancer vaccine not only reflects its scientific capabilities but also contributes to a broader, international movement towards innovative cancer therapies. This progression is poised to reshape global cancer treatment protocols, offering hope for more effective and accessible care worldwide.
Expert Opinions
The development of Russia’s mRNA-based cancer vaccine has garnered attention from both the medical community and government officials.
Insights from Leading Oncologists and Medical Researchers on the Vaccine’s Potential Efficacy and Safety
Leading oncologists have expressed cautious optimism regarding the vaccine’s potential. Dr. Andrey Kaprin, General Director of the Radiology Medical Research Center of the Russian Ministry of Health, highlighted that preclinical studies have demonstrated the vaccine’s ability to suppress tumor growth and reduce metastasis risk. He emphasized that while these results are promising, comprehensive clinical trials are essential to fully assess the vaccine’s efficacy and safety in humans.
Medical researchers have noted that mRNA vaccine technology allows for rapid development and personalization, enabling the vaccine to be tailored to individual tumor profiles. This personalization could enhance the immune system’s ability to target and destroy cancer cells effectively. However, experts also caution that the long-term effects and potential side effects of such vaccines need thorough investigation through clinical trials.
Statements from Russian Health Officials and Scientists Involved in the Project
Russian health officials have been vocal about the significance of this development. President Vladimir Putin announced that Russian scientists are close to creating cancer vaccines that could soon be available to the public, underscoring the government’s support for innovative medical research.
Dr. Kaprin also mentioned that the vaccine is expected to be distributed to patients free of charge, with plans to launch it in general circulation in early 2025. He stated, “We have developed our own mRNA vaccine against cancer, and it will be distributed to patients free of charge.”
While the Russian mRNA-based cancer vaccine presents a promising advancement in oncology, experts agree that further clinical trials are necessary to establish its efficacy and safety fully. The commitment from Russian health officials to provide the vaccine free of charge reflects a significant step toward accessible cancer treatment.
Challenges and Considerations
The development and deployment of mRNA-based cancer vaccines, such as Russia’s recent initiative, present both promising opportunities and significant challenges.
Potential Obstacles in Large-Scale Production and Distribution
Scaling up the production of mRNA vaccines involves several complexities:
- Manufacturing Complexity: Producing mRNA vaccines requires sophisticated technology and stringent conditions to ensure stability and efficacy. Establishing facilities that meet these requirements on a large scale demands substantial investment and technical expertise.
- Supply Chain Logistics: The distribution of mRNA vaccines necessitates a reliable cold chain to maintain their stability, often requiring ultra-low temperature storage. Implementing such infrastructure, especially across vast regions, poses logistical challenges that could impede timely delivery to patients.
- Quality Control: Maintaining consistent quality across large production batches is crucial. Variations can affect vaccine efficacy and safety, necessitating rigorous quality assurance protocols that can be resource intensive.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations in the Deployment of a New Vaccine
Introducing a novel mRNA cancer vaccine involves navigating complex ethical and regulatory landscapes:
- Regulatory Approval: Gaining approval from health authorities requires comprehensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. This process can be time-consuming, and expedited pathways must still adhere to rigorous standards to ensure public safety.
- Ethical Distribution: Ensuring equitable access to the vaccine raises ethical questions, particularly in preventing disparities between different socioeconomic groups. Strategies must be developed to prioritize distribution without discrimination.
- Informed Consent: Patients must be fully informed about the benefits and potential risks associated with receiving a new vaccine. Transparent communication is essential to uphold patient autonomy and trust.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Ethical deployment includes commitments to post-vaccination surveillance to monitor long-term effects, ensuring ongoing patient safety and addressing any emerging concerns promptly.
While the advent of mRNA-based cancer vaccines marks a significant advancement in oncology, addressing the challenges of large-scale production, distribution, and ethical deployment is essential to realize their full potential in improving public health outcomes.
Conclusion
Russia’s recent announcement of developing an mRNA-based cancer vaccine marks a significant advancement in oncology. The vaccine is slated for free distribution to patients starting in early 2025, reflecting Russia’s commitment to accessible healthcare. Pre-clinical trials have demonstrated its potential to suppress tumor development and prevent metastasis. This development positions Russia alongside other nations exploring mRNA technology for cancer treatment, highlighting a global shift towards innovative cancer therapies.
The introduction of mRNA-based cancer vaccines signifies a transformative phase in cancer treatment. By harnessing the body’s immune system to target and eliminate cancer cells, these vaccines offer a personalized and potentially more effective approach compared to traditional treatments. As research progresses and clinical trials advance, the integration of such vaccines into standard oncology practices could lead to improved survival rates and quality of life for patients worldwide.
The complexity of cancer necessitates a unified global effort in research and development. Collaborations across borders can expedite the discovery of innovative treatments, share valuable insights, and pool resources to overcome challenges. Russia’s initiative exemplifies the potential benefits of international cooperation in the fight against cancer, and it is imperative that such collaborative endeavors continue to advance the field.
Call to Action
We value your perspective on this groundbreaking development in cancer treatment. Please share your thoughts, questions, or experiences related to mRNA-based cancer vaccines in the comments section below. Your engagement fosters a community of informed individuals dedicated to advancing healthcare.
Stay informed about the latest medical breakthroughs and health news by subscribing to our blog. Receive timely updates on developments in cancer research, treatment options, and health policies directly to your inbox. Join our community committed to promoting health and well-being through knowledge and awareness.















1 Comment