What are the main critiques of social contract theory?
What are the main critiques of social contract theory?
Read lessSign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
What are the main critiques of social contract theory?
What are the main critiques of social contract theory?
Read lessHow do you choose the right pet insurance plan?
How do you choose the right pet insurance plan?
Read lessChoosing the right pet insurance plan requires careful consideration of your pet’s needs, your financial situation, and the coverage offered by different providers. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the best choice: 1. Assess Your Pet’s Needs Age: Older pets may require more comprehensiveRead more
Choosing the right pet insurance plan requires careful consideration of your pet’s needs, your financial situation, and the coverage offered by different providers. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make the best choice:
Make a list of your priorities (e.g., emergency care, chronic conditions, wellness checks) and use comparison tools or charts provided by insurance websites to find a plan that aligns with them.
See lessThe haka is a traditional Māori ceremonial dance or challenge originating from the indigenous people of New Zealand. It is characterized by vigorous movements, rhythmic chanting, and often fierce facial expressions, such as protruding tongues and bulging eyes. Traditionally performed by warriors befRead more
The haka is a traditional Māori ceremonial dance or challenge originating from the indigenous people of New Zealand. It is characterized by vigorous movements, rhythmic chanting, and often fierce facial expressions, such as protruding tongues and bulging eyes. Traditionally performed by warriors before battle, the haka was intended to intimidate opponents while also expressing the strength, unity, and determination of the performers.
There are various types of haka, each with its specific purpose and meaning:
One of the most famous haka is “Ka Mate,” composed in the early 19th century by the Māori chief Te Rauparaha. It celebrates survival and is commonly performed by the All Blacks. Its words convey the triumph of life over death.
Haka is more than a dance; it’s a profound expression of emotion, culture, and identity.
See lessWhat is the significance of existentialism in modern philosophy?
What is the significance of existentialism in modern philosophy?
Read lessExistentialism holds profound significance in modern philosophy as it addresses fundamental questions about human existence, freedom, and individual meaning in a world that often seems chaotic or indifferent. Its impact spans not only philosophy but also literature, art, psychology, and political thRead more
Existentialism holds profound significance in modern philosophy as it addresses fundamental questions about human existence, freedom, and individual meaning in a world that often seems chaotic or indifferent. Its impact spans not only philosophy but also literature, art, psychology, and political thought. Below are the key reasons why existentialism is significant:
Existentialism’s enduring relevance lies in its confrontation with timeless human dilemmas—freedom, choice, alienation, and the search for purpose. By addressing these issues, it provides a philosophical foundation for navigating the complexities of modern life and continues to inspire individuals and intellectual movements alike.
See lessWhat are grap restrictions?
GRAP Stage 3 entails a ban on non-essential construction work. Classes up to grade V are required to shift to hybrid mode under Stage 3. Parents and students have the option to choose online education wherever available. Under Stage 3, the use of BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel cars (4-wheelers) is rRead more
GRAP Stage 3 entails a ban on non-essential construction work. Classes up to grade V are required to shift to hybrid mode under Stage 3. Parents and students have the option to choose online education wherever available.
Under Stage 3, the use of BS-III petrol and BS-IV diesel cars (4-wheelers) is restricted in Delhi and nearby NCR districts. Persons with disabilities are exempt.
Stage 3 also bans non-essential diesel-operated medium goods vehicles with BS-IV or older standards in Delhi. The Stage 3 of GRAP was lifted on December 27 after a marked improvement in Delhi’s air quality following day-long rainfall in the national capital.
Throughout 2024, Delhi recorded the highest number of ‘severe’ AQI days since 2022, with 17 days exceeding an AQI of 400. Additionally, 70 days were classified as ‘very poor’. Not a single ‘good’ air quality day was recorded in 2024, a first since 2018.
See lessYes, it is possible to prepare for the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE) while pursuing a PhD, but it requires careful planning, time management, and dedication. Here are some considerations and tips for balancing both: 1. Understand the Commitment Required for Both PhD: A PhD demands significanRead more
Yes, it is possible to prepare for the UPSC Civil Services Examination (CSE) while pursuing a PhD, but it requires careful planning, time management, and dedication. Here are some considerations and tips for balancing both:
Several candidates such as Anna Sinha have successfully cleared UPSC while pursuing higher studies, including PhDs. Their success underscores the importance of discipline and a strategic approach.
With proper planning and perseverance, it is feasible to balance both pursuits effectively.
See lessThe Charter Act of 1833 made the Governor-General of Bengal the Governor-General of India. Key Provisions of the Act: Centralization of Power: It vested legislative power exclusively in the Governor-General in Council, thereby centralizing authority. First Governor-General of India: Lord William BenRead more
The Charter Act of 1833 made the Governor-General of Bengal the Governor-General of India.
This act marked a significant step in consolidating British rule in India.
See lessWho among the following rulers of medieval Gujarat surrendered Diu to the Portuguese? [2023]
Who among the following rulers of medieval Gujarat surrendered Diu to the Portuguese? [2023]
Read lessThe correct answer is: Bahadur Shah. Explanation: Bahadur Shah, the Sultan of Gujarat, is the ruler who surrendered Diu to the Portuguese in the early 16th century. In 1535, Bahadur Shah faced a defeat against the Portuguese and, under pressure, surrendered Diu to them in exchange for peace. This evRead more
The correct answer is: Bahadur Shah.
Bahadur Shah, the Sultan of Gujarat, is the ruler who surrendered Diu to the Portuguese in the early 16th century.
It was Bahadur Shah who surrendered Diu to the Portuguese after facing defeat.
See lessWhat is Dunning-Kruger Effect?
What is Dunning-Kruger Effect?
Read lessThe Dunning-Kruger Effect is a cognitive bias in which people with low ability or knowledge in a specific area overestimate their own competence. Essentially, individuals who are less skilled or knowledgeable in a subject tend to have an inflated sense of their ability, while those who are more expeRead more
The Dunning-Kruger Effect is a cognitive bias in which people with low ability or knowledge in a specific area overestimate their own competence. Essentially, individuals who are less skilled or knowledgeable in a subject tend to have an inflated sense of their ability, while those who are more experienced or knowledgeable may underestimate their own expertise.
This effect occurs because people with limited knowledge or skills in a domain often lack the awareness to recognize their shortcomings. The Dunning-Kruger Effect was identified in 1999 by psychologists David Dunning and Justin Kruger, who conducted a series of experiments that demonstrated this phenomenon.
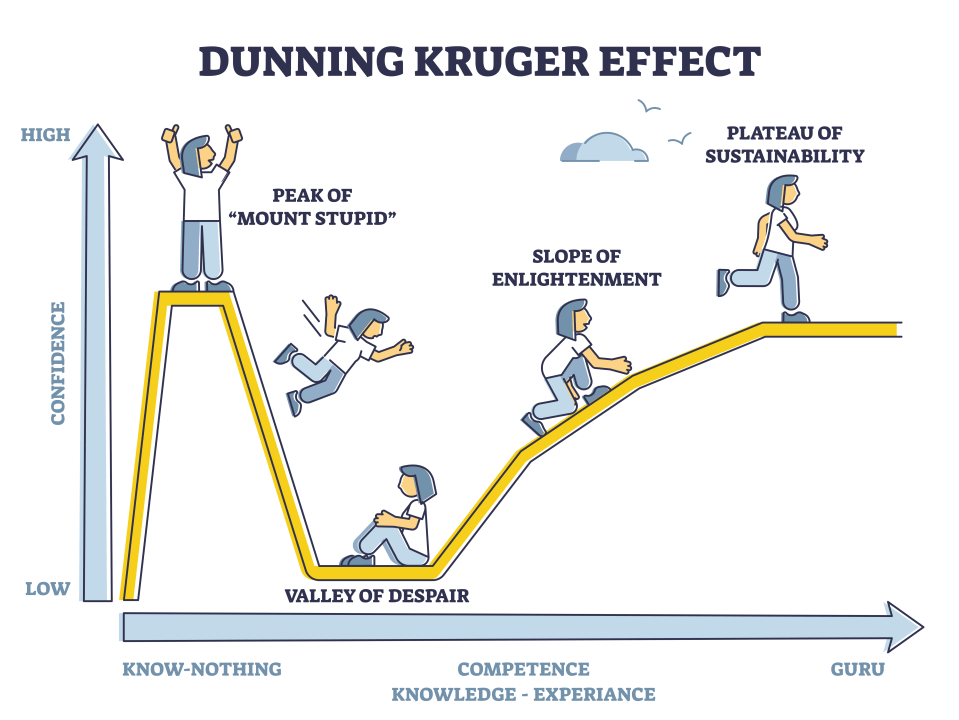
Source: LinkedIn
Key aspects of the Dunning-Kruger Effect include:
In summary, the Dunning-Kruger Effect highlights the paradox that those with the least knowledge in a domain are often the most confident about their skills in it.
See lessIs Ratan Tata’s legacy truly as inspiring as it seems?
Is Ratan Tata’s legacy truly as inspiring as it seems?
Read lessRatan Tata is widely celebrated as one of India’s most respected and influential business leaders, and much of his reputation is grounded in his unique approach to business and philanthropy. His contributions extend beyond profitability, impacting areas like social welfare, ethics, and national pridRead more
Ratan Tata is widely celebrated as one of India’s most respected and influential business leaders, and much of his reputation is grounded in his unique approach to business and philanthropy. His contributions extend beyond profitability, impacting areas like social welfare, ethics, and national pride, which is why he’s often held in high regard. However, the narrative of greatness often simplifies complex realities. Here are some nuanced aspects to consider:

Ratan Tata’s reputation is based on genuine contributions to India’s economy and society, although, like any leader, he faced challenges and controversies. His legacy is complex, encompassing both the achievements and the lessons learned from his ambitions.
See less
Social contract theory, a cornerstone of political philosophy, posits that individuals consent, either explicitly or implicitly, to form a society and establish a government to protect their rights and ensure order. While influential, the theory has been subjected to various critiques. Below are theRead more
Social contract theory, a cornerstone of political philosophy, posits that individuals consent, either explicitly or implicitly, to form a society and establish a government to protect their rights and ensure order. While influential, the theory has been subjected to various critiques. Below are the main criticisms:
1. Historical Inaccuracy
2. Implied Consent
3. Exclusionary Basis
4. Assumption of a Pre-Social State
5. Overemphasis on Rationality
6. Neglect of Power Dynamics
7. Idealism vs. Realism
8. Ambiguity in Enforcement
9. Individualism and Atomism
10. Assumption of Universality
11. Moral Relativism
While social contract theory remains influential, these critiques highlight its limitations and encourage more nuanced approaches to understanding society, governance, and justice. Modern theories often incorporate insights from feminist, communitarian, and critical perspectives to address these shortcomings.
See less