What is “chain-of-thought” ?
What is “chain-of-thought” ?
Read lessSign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
What is “chain-of-thought” ?
What is “chain-of-thought” ?
Read lessHow does the “chain-of-thought” reasoning improve the accuracy of DeepSeek-R1 ?
How does the “chain-of-thought” reasoning improve the accuracy of DeepSeek-R1 ?
Read lessWhat is DeepSeek R1?
What is DeepSeek R1?
Read lessDeepSeek R1 is an advanced AI language model developed by the Chinese startup DeepSeek. It is designed to enhance problem-solving and analytical capabilities, demonstrating performance comparable to leading models like OpenAI's GPT-4. Key Features: Reinforcement Learning Approach: DeepSeek R1 employRead more
DeepSeek R1 is an advanced AI language model developed by the Chinese startup DeepSeek. It is designed to enhance problem-solving and analytical capabilities, demonstrating performance comparable to leading models like OpenAI’s GPT-4. Key Features:
Performance Highlights:
Accessing DeepSeek R1:
DeepSeek R1 represents a significant advancement in AI language models, combining innovative training methods with open-source accessibility and cost-effectiveness.
See lessWhat is the future of Artificial Intelligence in FinTech?
The Future of Artificial Intelligence in FinTech Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the financial technology (FinTech) industry, enhancing efficiency, security, and customer experiences. As AI continues to evolve, its future in FinTech looks promising, with several transformative trendsRead more
The Future of Artificial Intelligence in FinTech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the financial technology (FinTech) industry, enhancing efficiency, security, and customer experiences. As AI continues to evolve, its future in FinTech looks promising, with several transformative trends and innovations.
1. Hyper-Personalization in Banking and Financial Services
AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants will provide real-time, personalized financial advice tailored to individual user behavior.
Robo-advisors will become more advanced, helping users make smarter investment decisions based on real-time market trends and personal risk appetite.
2. Enhanced Fraud Detection and Cybersecurity
AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms will continuously analyze financial transactions to detect fraudulent activities.
Biometric authentication (facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, voice verification) will further strengthen security measures.
3. AI-Driven Risk Assessment and Credit Scoring
AI will revolutionize loan approvals and credit scoring by analyzing alternative data sources like social media activity, purchase history, and online behavior.
Traditional credit models will become more inclusive, allowing individuals with limited credit history to access financial services.
4. Algorithmic Trading and Wealth Management
AI-powered algorithmic trading will become more sophisticated, enabling real-time investment strategies with minimal human intervention.
Hedge funds and financial institutions will rely on AI-driven analytics to optimize portfolios and predict market movements.
5. Automation of Regulatory Compliance (RegTech)
AI will streamline regulatory compliance by automatically analyzing legal requirements and ensuring that financial institutions adhere to global regulations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) will help banks process complex legal documents efficiently.
6. Conversational AI and Voice Banking
AI-powered voice assistants will enable customers to perform banking transactions through voice commands, improving accessibility and convenience.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) will enhance chatbots to handle complex financial queries more effectively.
7. Blockchain and AI Integration for Secure Transactions
AI and blockchain will work together to provide tamper-proof, automated financial contracts (smart contracts).
Decentralized AI-powered fraud detection will help secure cryptocurrency transactions and digital payments.
8. AI-Powered Insurance (InsurTech)
AI will help insurers assess risks more accurately, leading to dynamic pricing models for insurance policies.
Automated claims processing and AI-driven underwriting will speed up approval times and reduce fraud.
9. Financial Inclusion and Microfinance
AI will facilitate microloans and financial services for unbanked populations by analyzing behavioral and digital transaction data.
Mobile AI-driven financial solutions will empower emerging markets and rural areas with better banking access.
10. Quantum Computing and AI in FinTech
The combination of AI and quantum computing will significantly enhance risk modeling, financial forecasting, and fraud detection.
Quantum algorithms will revolutionize financial markets by processing massive amounts of data in real-time.
The future of AI in FinTech is dynamic and transformative, driving innovation in banking, insurance, investment, and cybersecurity. As AI models become more sophisticated and ethical, financial services will become more secure, efficient, and customer-centric. However, addressing data privacy, AI bias, and regulatory challenges will be critical to ensuring sustainable AI adoption in FinTech.
See lessIs artificial intelligence good for Society?
Is artificial intelligence good for Society?
Read lessArtificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to be both beneficial and challenging for society, depending on how it is developed and applied. Here are some aspects to consider: Positive Impacts: Healthcare: AI can help with early diagnosis, personalized treatments, and drug development. It can assRead more
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to be both beneficial and challenging for society, depending on how it is developed and applied. Here are some aspects to consider:
Positive Impacts:
Healthcare:
AI can help with early diagnosis, personalized treatments, and drug development. It can assist doctors in identifying conditions that may not be easily detectable, improving health outcomes.
Automation and Productivity:
AI can automate repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex, creative, or strategic work. This can increase productivity and innovation.
Environmental Sustainability:
AI can optimize energy usage, predict climate patterns, and improve waste management, all of which contribute to environmental protection and sustainability.
Education and Accessibility:
AI can personalize learning experiences for students, helping those with disabilities and providing access to education in remote areas.
Safety and Security:
AI systems can be used in areas like cybersecurity, fraud detection, and disaster response, enhancing safety and security in society.
Challenges and Concerns:
Job Displacement:
Automation driven by AI could displace many jobs, especially in sectors like manufacturing, transportation, and customer service. This can lead to unemployment and income inequality.
Bias and Discrimination:
AI systems may perpetuate biases if they are trained on biased data. This can lead to unfair outcomes, particularly in areas like hiring, law enforcement, and lending.
Privacy and Surveillance:
AI can be used for surveillance, potentially infringing on individual privacy. There are concerns about how personal data is collected, stored, and used by AI systems.
Ethical and Moral Issues:
AI systems make decisions based on algorithms, but these decisions might lack empathy and moral consideration. Determining who is responsible for an AI’s actions (such as in autonomous vehicles) is also a complex issue.
Security Risks:
AI can be used maliciously, such as for creating deepfakes, cyberattacks, or autonomous weapons, posing threats to security.
Conclusion:
AI has the potential to greatly benefit society, but its implementation needs careful regulation, ethical considerations, and societal awareness. If developed responsibly, AI could help tackle some of humanity’s greatest challenges, but it also requires safeguards to minimize the risks and negative consequences.
Why is df.corr() giving “ValueError: could not convert string to float” ?
To get rid of this error use: numeric_only=True df.corr(numeric_only=True) This is ignoring the columns that are 'object' type while calculating correlation.
To get rid of this error use: numeric_only=True
df.corr(numeric_only=True)This is ignoring the columns that are ‘object’ type while calculating correlation.
See lessWhy only the cells in the first row of Heat Map displaying annotation not the other cells?
Why only the cells in the first row of Heat Map displaying annotation not the other cells?
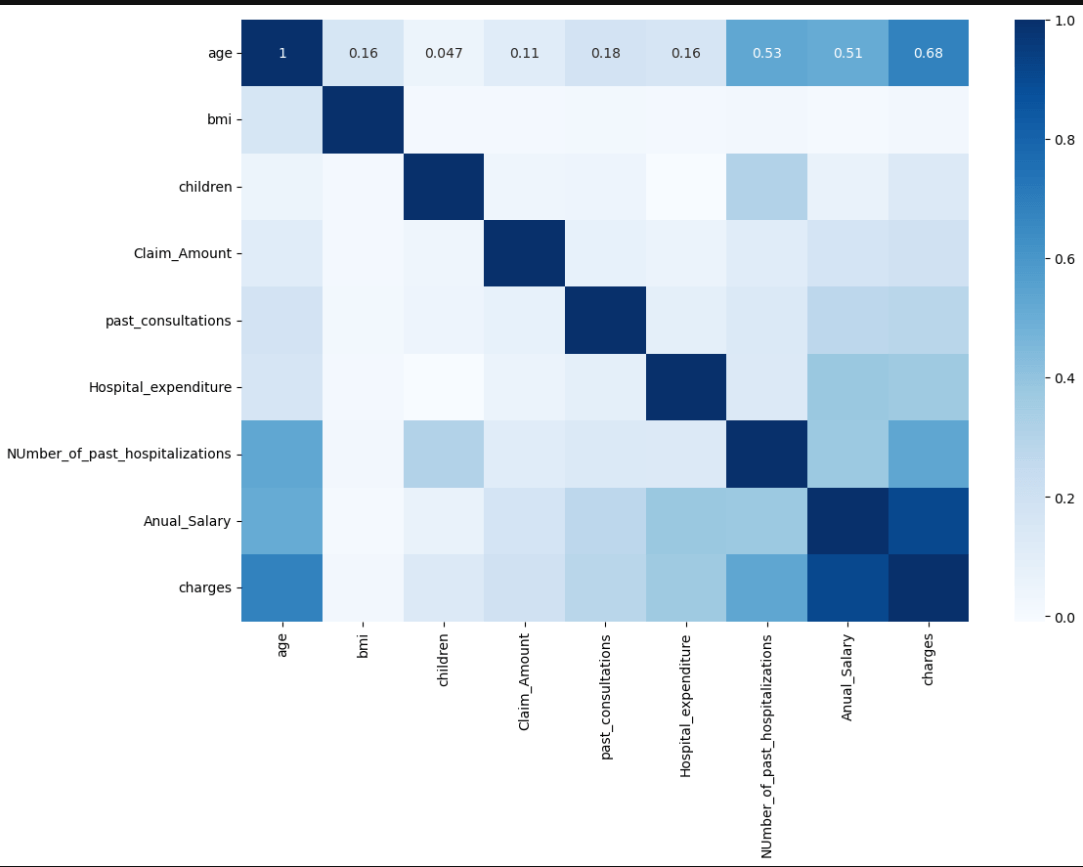
This issue could be due to an outdated version of Seaborn. You can resolve it by updating Seaborn with the following command: pip install seaborn --upgrade
This issue could be due to an outdated version of Seaborn. You can resolve it by updating Seaborn with the following command:
pip install seaborn --upgrade
How Can GPS Tracking in Sydney Improve Fleet Efficiency?
How Can GPS Tracking in Sydney Improve Fleet Efficiency?
Read lessGPS tracking in Sydney has become a game-changer for businesses looking to boost their fleet efficiency. With GPS tracking technology, fleet managers gain real-time insight into vehicle locations, allowing them to monitor and manage operations with precision. This technology is especially beneficialRead more
GPS tracking in Sydney has become a game-changer for businesses looking to boost their fleet efficiency. With GPS tracking technology, fleet managers gain real-time insight into vehicle locations, allowing them to monitor and manage operations with precision. This technology is especially beneficial in Sydney, where traffic congestion can lead to significant delays. With GPS tracking, businesses can optimize routes, avoid high-traffic areas, and reduce travel time, ensuring timely deliveries and happier customers.
Beyond navigation, GPS tracking in Sydney also helps cut fuel costs by reducing idle time and ensuring vehicles take the most efficient routes. It enhances driver accountability by monitoring driving behaviors like speed, braking, and acceleration, which can lower accident risks and reduce maintenance needs.
By adopting GPS tracking, companies can also boost customer satisfaction. Real-time tracking allows businesses to provide customers with accurate arrival estimates, enhancing service quality. In summary, GPS tracking in Sydney enables better decision-making, reduces operational costs, and supports safer driving practices, making it a valuable tool for any business managing a fleet in the city.
For more information, please visit: https://www.netcorp.com.au/
See lessThe discoverer of methane and the inventor of the electric battery was Alessandro Volta (1745–1827), an Italian physicist, chemist, and pioneer in electricity. Methane Discovery: Year: 1776 Volta discovered methane while studying marsh gases from Lake Maggiore in Italy. He identified it as a flammabRead more
The discoverer of methane and the inventor of the electric battery was Alessandro Volta (1745–1827), an Italian physicist, chemist, and pioneer in electricity.
Methane Discovery:
Year: 1776
Volta discovered methane while studying marsh gases from Lake Maggiore in Italy. He identified it as a flammable gas and demonstrated its combustion properties.
Electric Battery Invention:
Year: 1800
Volta invented the Voltaic Pile, the first electric battery capable of providing a steady current. It consisted of alternating layers of zinc and copper discs separated by cloth or cardboard soaked in saltwater.
Volta’s work laid the foundation for modern electrochemistry and electricity. The unit of electric potential, the volt, is named in his honor.
See lessfirst one open the app and go to setting and scroll down with saw the sharing of this app this is feature
first one open the app and go to setting and scroll down with saw the sharing of this app this is feature
See less
Chain-of-thought (CoT) is a reasoning technique used in artificial intelligence (AI) and human cognition to break down complex problems into smaller, logical steps. It helps models, like me, generate more accurate and coherent responses by explicitly outlining intermediate reasoning steps rather thaRead more
Chain-of-thought (CoT) is a reasoning technique used in artificial intelligence (AI) and human cognition to break down complex problems into smaller, logical steps. It helps models, like me, generate more accurate and coherent responses by explicitly outlining intermediate reasoning steps rather than jumping directly to an answer.
In AI and Machine Learning:
In AI, Chain-of-Thought prompting refers to a method where a model is guided to think step-by-step before arriving at a conclusion. This improves its ability to solve math problems, logical reasoning tasks, and commonsense reasoning challenges.
For example:
Without CoT:
Q: If a person buys a pencil for $1.50 and an eraser for $0.50, how much do they spend in total?
A: $2.00
With CoT:
Q: If a person buys a pencil for $1.50 and an eraser for $0.50, how much do they spend in total?
A: $2.00
By explicitly listing steps, AI reduces errors and enhances interpretability.
In Human Thinking:
In everyday life, people use chain-of-thought reasoning to solve problems, make decisions, and analyze situations methodically. For example, when planning a trip, you might consider:
This structured approach ensures well-thought-out decisions rather than impulsive choices.
Why Is Chain-of-Thought Important?
- Boosts problem-solving accuracy by breaking tasks into manageable steps.
- Reduces errors in AI models and logical reasoning.
- Enhances explainability, making complex reasoning easier to follow.
- Mimics human thinking for better AI-human interaction.
See less