What is the speed of light?
What is the speed of light?
Read lessSign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
What are the types of simple machines?
What are the types of simple machines?
Read lessWhat is the process of photosynthesis in plants?
What is the process of photosynthesis in plants?
Read lessHere's a simplified explanation of photosynthesis: Step 1: Plants Absorb Water and Carbon Dioxide Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots and carbon dioxide from the air through their leaves. Step 2: Plants Absorb Light Energy Plants absorb light energy from the sun. Step 3: Plants ConRead more
Here’s a simplified explanation of photosynthesis:
Step 1: Plants Absorb Water and Carbon Dioxide
Plants absorb water from the soil through their roots and carbon dioxide from the air through their leaves.
Step 2: Plants Absorb Light Energy
Plants absorb light energy from the sun.
Step 3: Plants Convert Light Energy into Food
Plants use the light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into a type of sugar that gives them energy.
Step 4: Plants Release Oxygen
As a byproduct of photosynthesis, plants release oxygen into the air.
Overall Equation
Water + Carbon Dioxide + Light Energy → Food (Sugar) + Oxygen
Photosynthesis is like a magic power that plants have, which helps them make their own food using sunlight, water, and air.
See lessWhat is a supernova, and how is it formed?
What is a supernova, and how is it formed?
Read lessA supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion that occurs when a star reaches the end of its life cycle. It is one of the most energetic events in the universe, releasing a vast amount of energy and often outshining entire galaxies for a short period. How a Supernova is Formed: Stellar EvolutionRead more
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion that occurs when a star reaches the end of its life cycle. It is one of the most energetic events in the universe, releasing a vast amount of energy and often outshining entire galaxies for a short period.
Supernovae are crucial in understanding stellar evolution and the chemical enrichment of galaxies, and they also serve as important cosmic distance markers in the study of the universe.
See lessWhat is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
What is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
Read lessribosome is a main crucial role play in a human cell its make and process of the protein in cell and also its two type of ribosomes 70s of ribosome and 80s of ribosome these are present in prokaryote and eukaryote
ribosome is a main crucial role play in a human cell its make and process of the protein in cell and also its two type of ribosomes 70s of ribosome and 80s of ribosome these are present in prokaryote and eukaryote
See lessHow do the phases of the moon occur?
How do the phases of the moon occur?
Read lessThe phases of the Moon occur due to the Moon's position relative to the Earth and the Sun as it orbits around the Earth. The Moon does not produce its own light; instead, it reflects sunlight. The phases result from the changing portion of the Moon's illuminated surface visible from Earth. Here's anRead more
The phases of the Moon occur due to the Moon’s position relative to the Earth and the Sun as it orbits around the Earth. The Moon does not produce its own light; instead, it reflects sunlight. The phases result from the changing portion of the Moon’s illuminated surface visible from Earth. Here’s an explanation of how the phases occur:
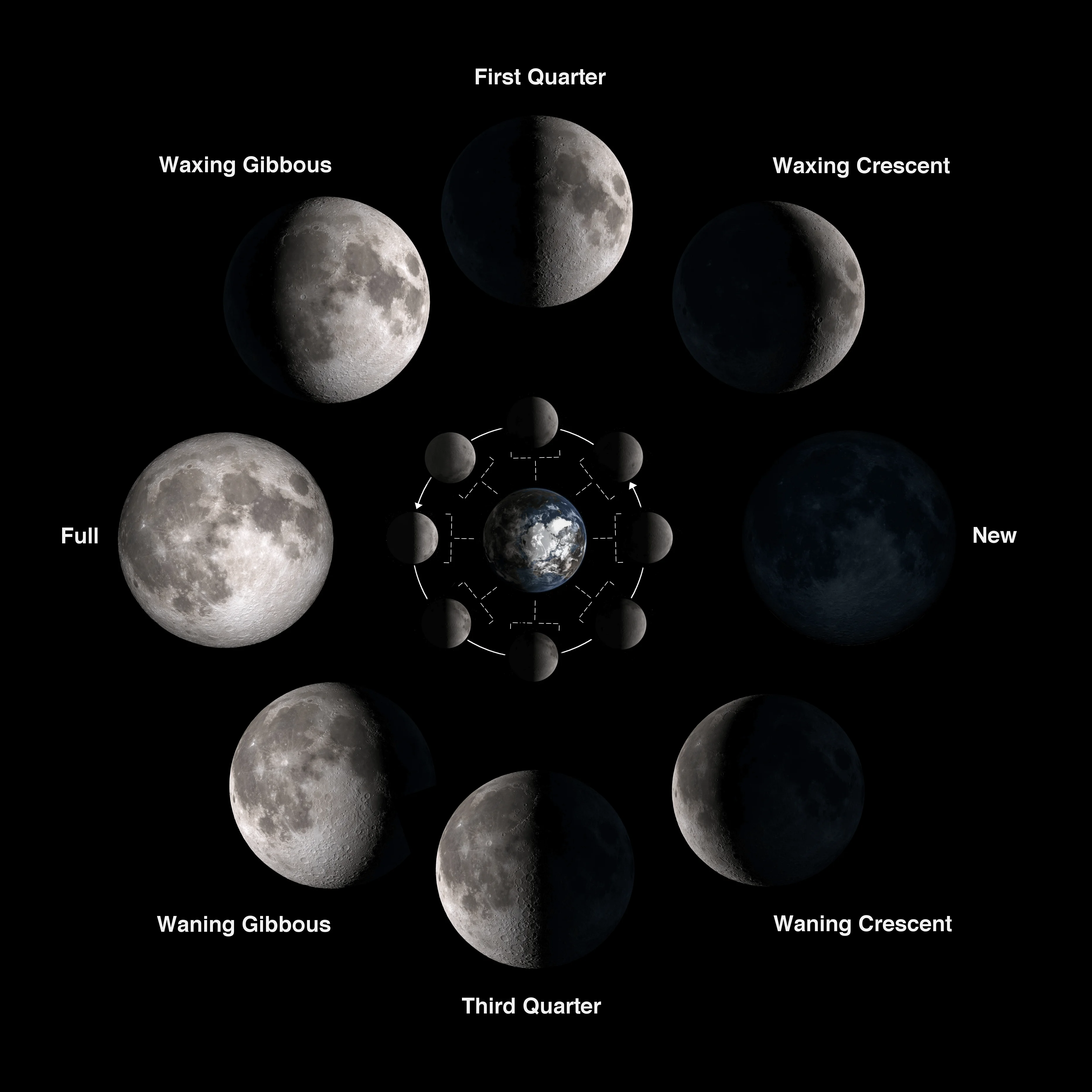

Source: NASA
This cycle, called a lunar month, takes about 29.5 days to complete.
See lessHow do plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis?
How do plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis?
Read lessPlants produce oxygen during photosynthesis, a process in which they convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. Here's how oxygen is produced: Step-by-Step Explanation Light Absorption: Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts absorbs light energy from the Sun. This energy is used to splitRead more
Plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis, a process in which they convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. Here’s how oxygen is produced:
How does the theory of evolution explain the diversity of life on Earth?
How does the theory of evolution explain the diversity of life on Earth?
Read lessThe theory of evolution explains the diversity of life on Earth by proposing that all species of living organisms have descended from common ancestors and have gradually changed over time through processes like natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow. These processes lead to the adRead more
The theory of evolution explains the diversity of life on Earth by proposing that all species of living organisms have descended from common ancestors and have gradually changed over time through processes like natural selection, genetic drift, mutation, and gene flow. These processes lead to the adaptation of organisms to their environments, resulting in the variety of life forms we see today.
The theory of evolution explains the diversity of life on Earth by showing how species change over time through a combination of genetic variation, selection, and inheritance. Over millions of years, these processes have led to the vast array of life forms that exist today, each adapted to its particular environment. Evolution provides a framework for understanding how all living organisms are connected through common ancestry and how diversity arises through continuous adaptation to changing conditions.
See less
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
speed of light c=3×10^8 meter/second in vacuum
See less