what is the role of nerve cell in human beings.
what is the role of nerve cell in human beings.
Read lessSign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
what is the role of nerve cell in human beings.
what is the role of nerve cell in human beings.
Read lessthe most smallest bone in human being
the most smallest bone in human being
Read lessThe smallest bone in the human body is the stapes bone, located in the middle ear. It is part of the ossicles, which are three tiny bones responsible for transmitting sound vibrations from the air to the inner ear. The stapes bone is roughly 0.1 inches (2.5 millimeters) in length and weighs only a fRead more
The smallest bone in the human body is the stapes bone, located in the middle ear. It is part of the ossicles, which are three tiny bones responsible for transmitting sound vibrations from the air to the inner ear. The stapes bone is roughly 0.1 inches (2.5 millimeters) in length and weighs only a few milligrams. Despite its small size, it plays a crucial role in hearing by transferring sound from the eardrum to the cochlea in the inner ear.
See lessWhat are the different types of chemical bonds?
What are the different types of chemical bonds?
Read lessChemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are several types of chemical bonds, each with unique properties and roles in chemical structures. The primary types include: Ionic Bond Definition: Formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to aRead more
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. There are several types of chemical bonds, each with unique properties and roles in chemical structures. The primary types include:
Each type of bond plays a crucial role in determining the properties and behavior of different substances. Understanding these bonds is essential for studying chemical reactions and the formation of various materials.
See lessWhat were the different types Dinosaurs present on the earth?
What were the different types Dinosaurs present on the earth?
Read lessDinosaurs were incredibly diverse and can be categorized into various types based on their physical characteristics, diet, and evolutionary lineage. Here's an overview of the main types of dinosaurs: Theropods Diet: Carnivorous (meat-eating). Characteristics: Bipedal, with sharp teeth and claws. ExaRead more
Dinosaurs were incredibly diverse and can be categorized into various types based on their physical characteristics, diet, and evolutionary lineage. Here’s an overview of the main types of dinosaurs:
These types highlight the incredible variety among dinosaurs, showcasing their adaptations to different environments and niches during the Mesozoic Era.
See lessIn the prenatal stage, your bones undergo a fascinating transformation as part of fetal development. Here's how your bones develop during this time: Mesenchymal Stage (Week 5-7) Formation of Mesenchyme: In early development, your skeleton starts as mesenchyme, a type of loose connective tissue madeRead more
In the prenatal stage, your bones undergo a fascinating transformation as part of fetal development. Here’s how your bones develop during this time:
This step-by-step transformation ensures that your bones are well-formed, strong, and capable of supporting your body after birth, while still allowing flexibility for growth and development.
See lessAdvancements in vaccine development and antiviral therapies can significantly mitigate the global burden of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infections in several ways: Prevention through Vaccination Development of Effective Vaccines: Creating vaccines that target HMPV can reduce the incidence of infectRead more
Advancements in vaccine development and antiviral therapies can significantly mitigate the global burden of human metapneumovirus (HMPV) infections in several ways:
Overall, advancements in vaccine development and antiviral therapies are crucial in reducing the incidence, severity, and economic impact of HMPV infections, contributing to better global health outcomes.
See lessdiscuss the working of heart in detail
discuss the working of heart in detail
Read lessThe heart is a muscular organ that functions as the central component of the circulatory system, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Its primary role is to supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and remove carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes. The heart operates in a highly coordRead more
The heart is a muscular organ that functions as the central component of the circulatory system, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Its primary role is to supply oxygen and nutrients to tissues and remove carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes. The heart operates in a highly coordinated manner, with distinct phases of contraction and relaxation. Here’s a detailed discussion on how the heart works:
The heart consists of four chambers:
The heart also contains several valves that control the flow of blood and prevent backflow:
The heart works through a continuous cycle of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole). The cycle ensures that blood flows in the right direction and is efficiently pumped throughout the body.
The heart’s pumping action is controlled by an electrical system that ensures the chambers contract in a coordinated manner. The major components of this system are:
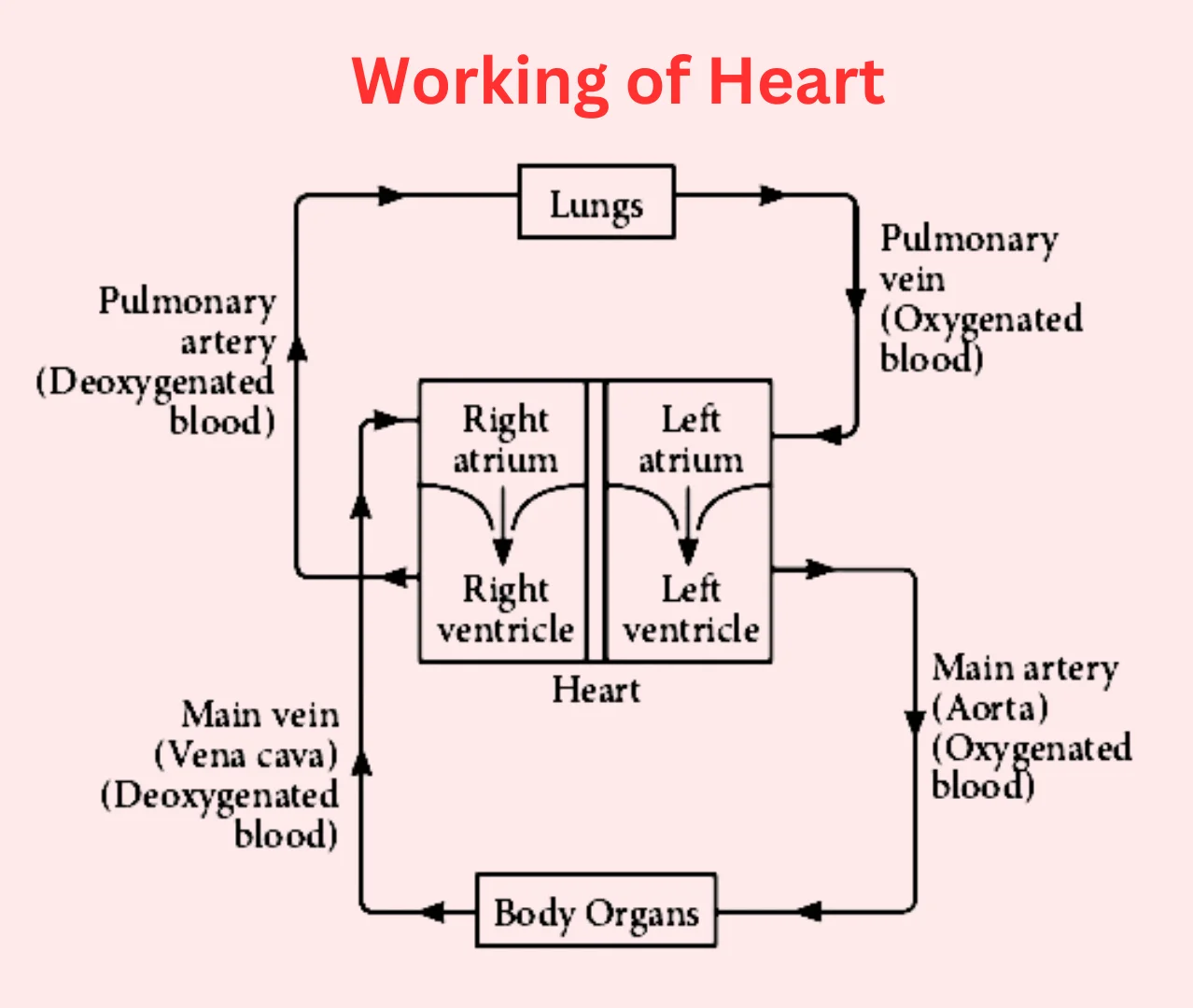
The heart rate is controlled by a combination of:
The heart can be affected by various diseases and conditions, including:
The heart functions as a pump that circulates blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products. Its intricate structure, along with its electrical and mechanical coordination, allows it to operate efficiently. Proper heart function is vital for overall health, and any disturbances in its working can lead to serious health conditions.
See lessExplain the 3 classes of levers
Explain the 3 classes of levers
Read lessLever is the force placed between the fulcrum and the load. If the load is closer to the fulcrum, researchers of movement in the load require less force. If the force is closer to the fulcrum, movement of the load requires more force.
Lever is the force placed between the fulcrum and the load. If the load is closer to the fulcrum, researchers of movement in the load require less force. If the force is closer to the fulcrum, movement of the load requires more force.
See lessConsider the following statements: ...Read more
Consider the following statements: [2023]
1. Ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase of flight.
2. Agni-V is a medium-range supersonic cruise missile, while BrahMos is a solid-fuelled intercontinental ballistic missile.
Let's evaluate the two statements: Statement 1: Ballistic missiles are typically rocket-propelled and follow a parabolic trajectory that reaches the upper atmosphere before re-entering and hitting the target at high speeds, often supersonic or hypersonic. Cruise missiles, on the other hand, are typiRead more
Let’s evaluate the two statements:
The statement that ballistic missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flight and cruise missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial phase is incorrect. In fact, it should be the other way around: Ballistic missiles are rocket-propelled throughout their flight, while cruise missiles are jet-powered for most of their flight.
Therefore, Statement 2 is also incorrect.
Both statements are incorrect.
The correct answer is: Neither 1 nor 2.
See lessWhich one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? [2023]
Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? [2023]
Read lessThe country that has its own satellite navigation system is Japan. Japan's satellite navigation system is called QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System), which provides satellite-based positioning and timing information, mainly in the Asia-Pacific region. Australia, Canada, and Israel do not have theirRead more
The country that has its own satellite navigation system is Japan. Japan’s satellite navigation system is called QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System), which provides satellite-based positioning and timing information, mainly in the Asia-Pacific region.
So, the correct answer is: Japan.
See less
Nerve cells, or neurons, play a critical role in the human body by serving as the fundamental units of the nervous system. Their primary function is to transmit information throughout the body, enabling communication between different parts of the body and the brain. Here's a detailed breakdown of tRead more
Nerve cells, or neurons, play a critical role in the human body by serving as the fundamental units of the nervous system. Their primary function is to transmit information throughout the body, enabling communication between different parts of the body and the brain. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their roles:
Nerve cells are essential for both voluntary and involuntary actions, allowing humans to interact with and respond to their environment, control bodily functions, and engage in complex mental activities.
See less