How did the planets in our solar system get their names?
How did the planets in our solar system get their names?
Read lessSign up to our innovative Q&A platform to pose your queries, share your wisdom, and engage with a community of inquisitive minds.
Log in to our dynamic platform to ask insightful questions, provide valuable answers, and connect with a vibrant community of curious minds.
Forgot your password? No worries, we're here to help! Simply enter your email address, and we'll send you a link. Click the link, and you'll receive another email with a temporary password. Use that password to log in and set up your new one!
Please briefly explain why you feel this question should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this answer should be reported.
Please briefly explain why you feel this user should be reported.
How did the planets in our solar system get their names?
How did the planets in our solar system get their names?
Read lessThe word ‘Denisovan’ is sometimes mentioned in media in reference to?
The word ‘Denisovan’ is sometimes mentioned in media in reference to?
Read lessThe word Denisovan refers to an extinct group of archaic humans that lived in parts of Asia around 50,000 to 200,000 years ago. They are named after the Denisova Cave in Siberia, where their fossils and genetic material were first discovered in 2008. Denisovans are closely related to Neanderthals anRead more
The word Denisovan refers to an extinct group of archaic humans that lived in parts of Asia around 50,000 to 200,000 years ago. They are named after the Denisova Cave in Siberia, where their fossils and genetic material were first discovered in 2008. Denisovans are closely related to Neanderthals and modern humans, and their DNA has been found in some modern populations, particularly among Melanesians, Aboriginal Australians, and some Southeast Asian groups.
In media, the term is often mentioned in discussions about human evolution, genetics, and the interbreeding between different human species in ancient times.
See lessWhat are sky charts?
What are sky charts?
Read lessA star chart is a celestial map of the night sky with astronomical objects laid out on a grid system. They are used to identify and locate constellations, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and planets. They have been used for human navigation since time immemorial.
A star chart is a celestial map of the night sky with astronomical objects laid out on a grid system. They are used to identify and locate constellations, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and planets. They have been used for human navigation since time immemorial.
See lessWhat is the pkate ye tonic theory??
What is the pkate ye tonic theory??
Read lessIt seems like you're referring to the "Plate Tectonic Theory." Here's a brief explanation: The Plate Tectonic Theory is a scientific concept that describes the large-scale movement of the Earth's lithosphere, which is divided into several large and small tectonic plates. These plates float on the seRead more
It seems like you’re referring to the “Plate Tectonic Theory.” Here’s a brief explanation:
The Plate Tectonic Theory is a scientific concept that describes the large-scale movement of the Earth’s lithosphere, which is divided into several large and small tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them and are constantly moving, albeit very slowly. This movement is driven by forces such as mantle convection, slab pull, and ridge push.
This theory has revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s geological processes, explaining the distribution of earthquakes, mountains, and volcanic activity.
See lessWhat is the continental drift theory??
What is the continental drift theory??
Read lessThe Continental Drift Theory is a geological hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912. It suggests that the Earth's continents were once part of a single, massive supercontinent called Pangaea, which began to break apart approximately 200 million years ago. Over time, the fragments drifted to tRead more
The Continental Drift Theory is a geological hypothesis proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912. It suggests that the Earth’s continents were once part of a single, massive supercontinent called Pangaea, which began to break apart approximately 200 million years ago. Over time, the fragments drifted to their current positions on the Earth’s surface.
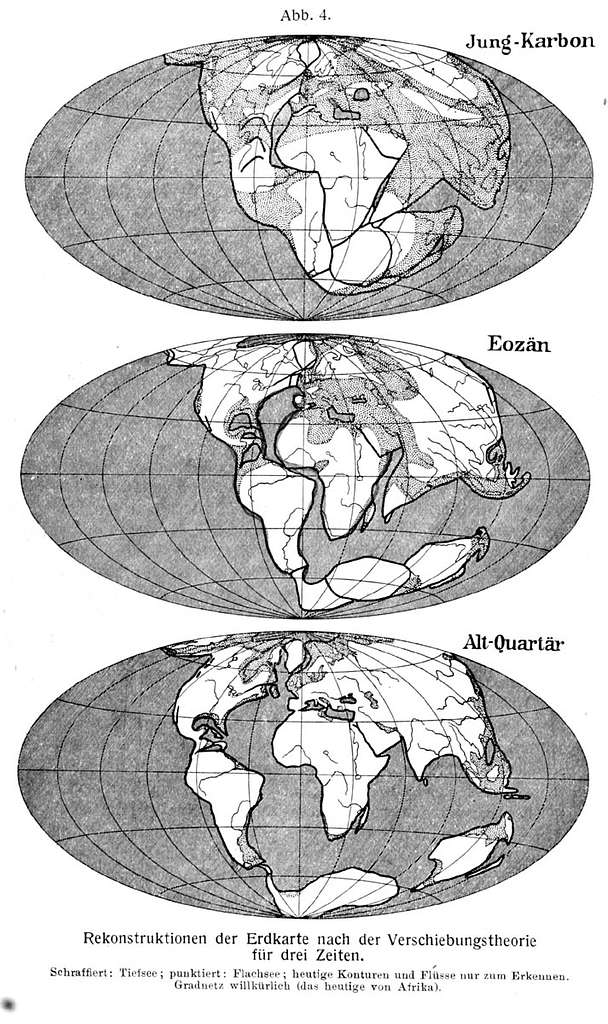
Source: Cambridge University Press
In essence, the Continental Drift Theory was a groundbreaking idea that transformed geology and paved the way for our current understanding of Earth’s structure and the movement of its continents.
See lessWhat are the various natural vegetations of North America
What are the various natural vegetations of North America
Read lessWhat are the different natural vegetations of South America?
What are the different natural vegetations of South America?
Read lessSouth America, with its diverse climate zones and ecosystems, is home to a wide variety of natural vegetation types. These vegetation zones are influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, rainfall, and temperature. The main natural vegetation types found across the continent include: 1. TropicRead more
South America, with its diverse climate zones and ecosystems, is home to a wide variety of natural vegetation types. These vegetation zones are influenced by factors such as latitude, altitude, rainfall, and temperature. The main natural vegetation types found across the continent include:
South America’s natural vegetation is incredibly diverse, reflecting the continent’s varied climates and geographic features. From the lush, biodiverse rainforests of the Amazon to the arid deserts of the Andes, the continent’s vegetation zones support an array of wildlife and are essential to the planet’s ecological balance. These ecosystems are also critical for human economies, providing resources for agriculture, timber, and tourism.
See lessWhich one of the following options is correct in respect of the given statements? [2023]Statement–I: The soil in tropical rain forests is rich in nutrients.Statement-II: The high ...Read more
Which one of the following options is correct in respect of the given statements? [2023]
Statement–I: The soil in tropical rain forests is rich in nutrients.
Statement-II: The high temperature and moisture of tropical rain forests cause dead organic matter in the soil to decompose quickly.
Correct Answer: Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct Explanation: Statement-I: "The soil in tropical rain forests is rich in nutrients." Incorrect. The soil in tropical rainforests is typically poor in nutrients. This is because heavy rainfall causes leaching, washing away nutrientsRead more
The soil in tropical rainforests is nutrient-poor, despite the rapid decomposition of organic matter due to the high temperature and moisture.
Thus, Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct.
With reference to the Earth’s atmosphere, which one of the following statements is correct? [2023]
With reference to the Earth’s atmosphere, which one of the following statements is correct? [2023]
Read lessCorrect Answer: Infrared waves are largely absorbed by water vapor that is concentrated in the lower atmosphere. Explanation: "The total amount of insolation received at the equator is roughly about 10 times that received at the poles." Incorrect. While there is a significant difference in insolatioRead more
Correct Answer: Infrared waves are largely absorbed by water vapor that is concentrated in the lower atmosphere.
Analysis: Bulgaria: Does not share a land border with Ukraine. Bulgaria is located south of Romania and separated from Ukraine by Romania. Czech Republic: Does not share a land border with Ukraine. The Czech Republic is located west of Slovakia, which lies between it and Ukraine. Hungary: Shares a lRead more
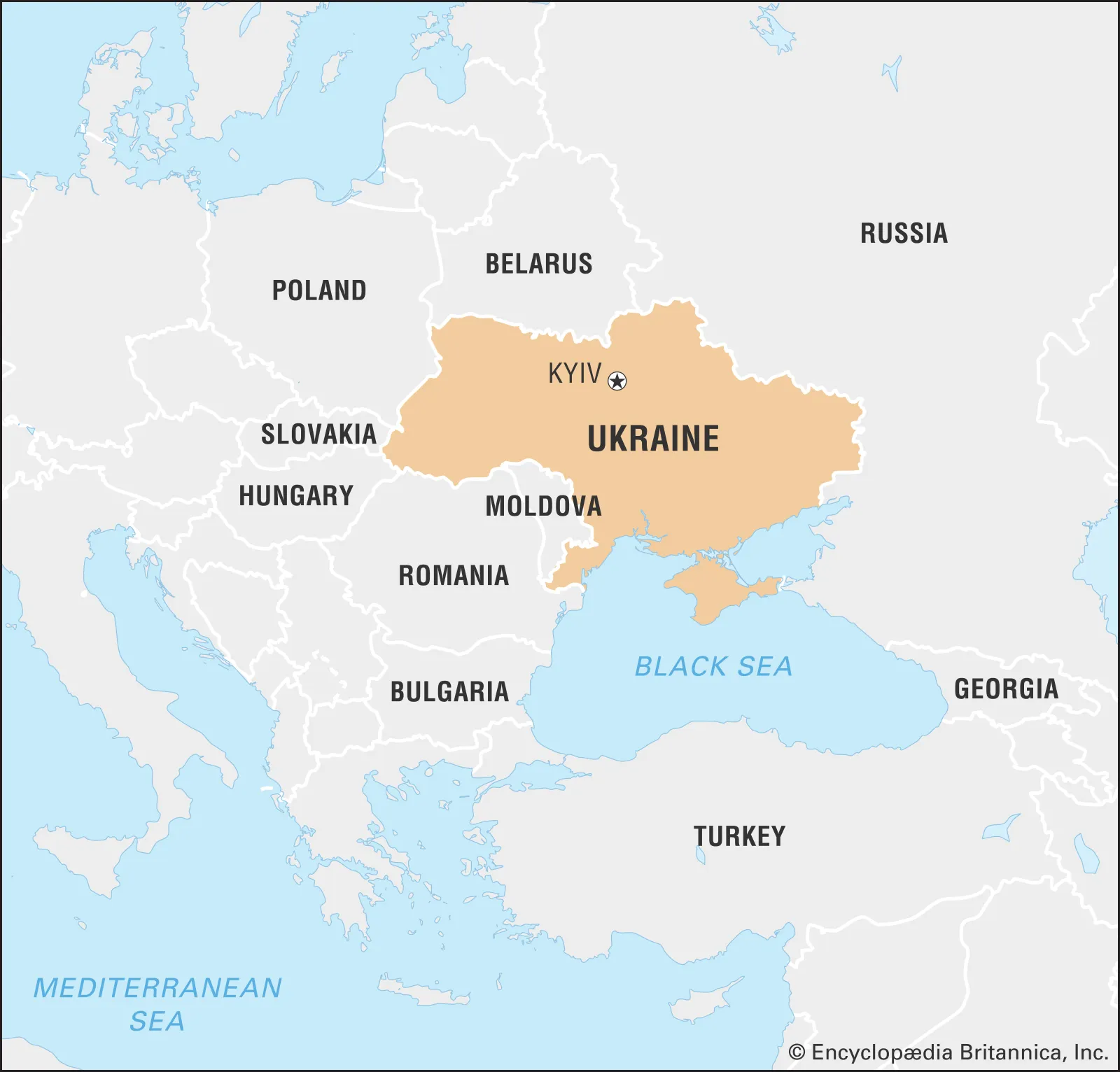
Source: Britannica
The correct countries that share a land border with Ukraine from the list are:
The names of the planets in our solar system are rooted in ancient mythology and cultural traditions. Here’s a breakdown: Mercury: Named after the Roman messenger god, Mercury, known for his speed, because the planet moves quickly across the sky. Venus: Named after the Roman goddess of love and beauRead more
The names of the planets in our solar system are rooted in ancient mythology and cultural traditions. Here’s a breakdown:
The tradition of naming planets after Roman and Greek gods reflects the influence of ancient astronomers, who sought to connect celestial objects with divine figures from their mythologies. This convention continues today for newly discovered celestial bodies.
See less